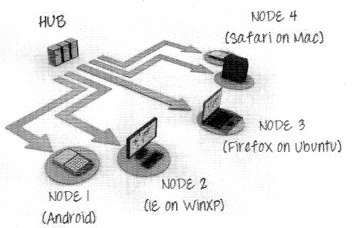
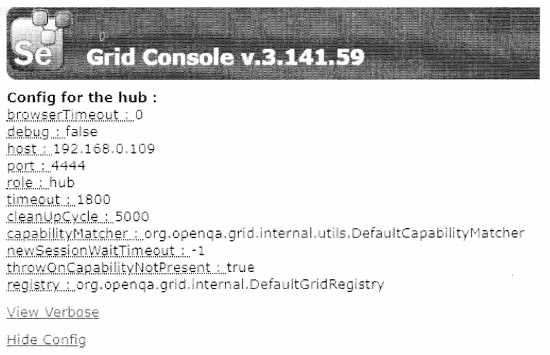
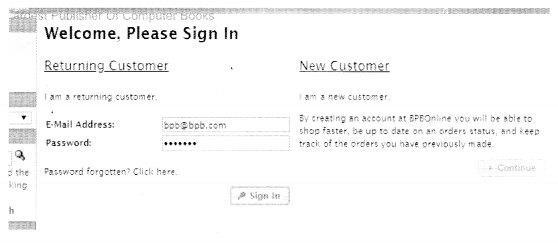
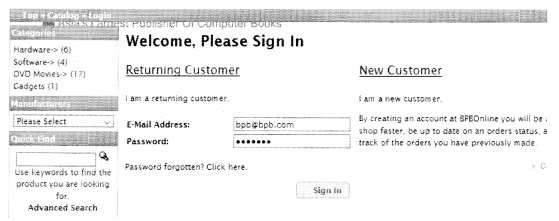
We have compiled most frequently asked Python Interview Questions which will help you with different expertise levels.
Python Interview Questions on HR Questions
Question 1:
Tell me about a time when you worked additional hours to finish a project.
Answer:
It’s important for your employer to see that you are dedicated to your work, and willing to put in extra hours when required or when a job calls for it. However, be careful when explaining. why you were called to work additional hours – for instance, did you have to stay late because you set goals poorly earlier in the process? Or on a more positive note, were you working additional hours because a client requested for a deadline to be moved up on short notice? Stress your competence and willingness to give 110% every time.
Question 2:
Tell me about a time when your performance exceeded the duties and requirements of your job.
Answer:
If you’re a great candidate for the position, this should be an easy question to answer – choose a time when you truly went above and beyond the call of duty, and put in additional work or voluntarily took on new responsibilities. Remain humble, and express gratitude for the learning opportunity, as well as confidence in your ability to give a repeat performance.
Question 3:
What is your driving attitude about work?
Answer:
There are many possible good answers to this question, and the interviewer primarily wants to see that you have a great passion for the job and that you will remain motivated in your career if hired. Some specific driving forces behind your success may include hard work, opportunity, growth potential, or success.
Question 4:
Do you take work home with you?
Answer:
It is important to first clarify that you are always willing to take work home when necessary, but you want to emphasize as well that it has not been an issue for you in the past. Highlight skills such as time management, goal-setting, and multitasking, which can all ensure that work is completed at work.
Question 5:
Describe a typical workday to me.
Answer:
There are several important components in your typical workday, and an interviewer may derive meaning from any or all of them, as well as from your ability to systematically lead him or her through the day. Start at the beginning of your day and proceed chronologically, making sure to emphasize steady productivity, time for review, goal-setting, and prioritizing, as well as some additional time to account for unexpected things that may arise.
Question 6:
Tell me about a time when you went out of your way at your previous job.
Answer:
Here it is best to use a specific example of the situation that required you to go out of your way, what your specific position would have required that you did, and how you went above that. Use concrete details, and be sure to include the results, as well as reflect on what you learned in the process.
Question 7:
Are you open to receiving feedback and criticisms on your job performance, and adjusting as necessary?
Answer:
This question has a pretty clear answer – yes – but you’ll need to display knowledge as to why this is important. Receiving feedback and criticism is one thing, but the most important part of that process is to then implement it into your daily work. Keep a good attitude, and express that you always appreciate constructive feedback.
Question 8:
What inspires you?
Answer:
You may find inspiration in nature, reading success stories, or mastering a difficult task, but it’s important that your inspiration is positively based and that you’re able to listen and tune into it when it appears. Keep this answer generally based in the professional world, but where applicable, it may stretch a bit into creative exercises in your personal life that, in turn, help you in achieving career objectives.
Question 9:
How do you inspire others?
Answer:
This may be a difficult question, as it is often hard to discern the effects of inspiration on others. Instead of offering a specific example of a time when you inspired someone, focus on general principles such as leading by example that you employ in your professional life. If possible, relate this to a quality that someone who inspired you possessed, and discuss the way you have modified or modeled it in your own work.
Question 10:
How do you make decisions?
Answer:
This is a great opportunity for you to wow your interviewer with your decisiveness, confidence, and organizational skills. Make sure that you outline a process for decision-making, and that you stress the importance of weighing your options, as well as in trusting intuition. If you answer this question skillfully and with ease, your interviewer will trust in your capability as a worker.
Question 11:
What are the most difficult decisions for you to make?
Answer:
Explain your relationship to decision-making, and a general synopsis of the process you take in making choices. If there is a particular type of decision that you often struggle with, such as those that involve other people, make sure to explain why that type of decision is tough for you, and how you are currently engaged in improving your skills.
Question 12:
When making a tough decision, how do you gather information?
Answer:
If you’re making a tough choice, it’s best to gather information from as many sources as possible. Lead the interviewer through your process of taking information from people in different areas, starting first with advice from experts in your field, feedback from coworkers or other clients, and looking analytically at your own past experiences.
Question 13:
Tell me about a decision you made that did not turn out well.
Answer:
Honesty and transparency are great values that your interviewer will appreciate – outline the choice you made, why you made it, the results of your poor decision – and finally (and most importantly!) what you learned from the decision. Give the interviewer reason to trust that you wouldn’t make a decision like that again in the future.
Question 14:
Are you able to make decisions quickly?
Answer:
You may be able to make decisions quickly, but be sure to communicate your skill in making sound, thorough decisions as well. Discuss the importance of making a decision quickly, and how you do so, as well as the necessity for each decision to first be well-informed.
Question 15:
Ten years ago, what were your career goals?
Answer:
In reflecting back on what your career goals were ten years ago, it’s important to show the ways in which you’ve made progress in that time. Draw distinct links between specific objectives that you’ve achieved, and speak candidly about how it felt to reach those goals. Remain positive, upbeat, and growth-oriented, even if you haven’t yet achieved all of the goals you set out to reach.
Question 16:
Tell me about a weakness you used to have, and how you changed it.
Answer:
Choose a non-professional weakness that you used to have, and outline the process you went through in order to grow past it. Explain the weakness itself, why it was problematic, the action steps you planned, how you achieved them, and the end result.
Question 17:
Tell me about your goal-setting process.
Answer:
When describing your goal-setting process, clearly outline the way that you create an outline for yourself. It may be helpful to offer an example of a particular goal you’ve set in the past, and use this as a starting point to guide the way you created action steps, check-in points, and how the goal was eventually achieved.
Question 18:
Tell me about a time when you solved a problem by creating actionable steps to follow.
Answer:
This question will help the interviewer to see how talented you are in outlining, problem resolution, and goal-setting. Explain thoroughly the procedure of outlining the problem, establishing steps to take, and then how you followed the steps (such as through check-in points along the way, or intermediary goals).
Question 19:
Where do you see yourself five years from now?
Answer:
Have some idea of where you would like to have advanced to in the position you’re applying for, over the next several years. Make sure that your future plans line up with you still working for the company, and stay positive about potential advancement. Focus on future opportunities, and what you’re looking forward to – but make sure your reasons for advancement are admirable, such as greater experience and the chance to learn, rather than simply being out for a higher salary.
Question 20:
When in a position, do you look for opportunities to promote?
Answer:
There’s a fine balance in this question – you want to show the interviewer that you have the initiative and motivation to advance in your career, but not at the expense of appearing opportunistic or selfishly motivated. Explain that you are always open to growth opportunities, and very willing to take on new responsibilities as your career advances.
Question 21:
On a scale of 1 to 10, how successful has your life been?
Answer:
Though you may still have a long list of goals to achieve, it’s important to keep this answer positively focused. Choose a high number between 7 and 9, and explain that you feel your life has been largely successful and satisfactory as a result of several specific achievements or experiences. Don’t go as high as a 10, as the interviewer may not believe your response or in your ability to reason critically.
Question 22:
What is your greatest goal in life?
Answer:
It’s okay for this answer to stray a bit into your personal life, but best if you can keep it professionally focused. While specific goals are great, if your personal goal doesn’t match up exactly with one of the company’s objectives, you’re better off keeping your goal a little more generic and encompassing, such as “success in my career” or “leading a happy and fulfilling life.” Keep your answer brief, and show a decisive nature – most importantly, make it clear that you’ve already thought about this question and know what you want.
Question 23:
Tell me about a time when you set a goal in your personal life and achieved it.
Answer:
The interviewer can see that you excel at setting goals in your professional life, but he or she also wants to know that you are consistent in your life and capable of setting goals outside of the office as well. Use an example such as making a goal to eat more healthily or to drink more water, and discuss what steps you outlined to achieve your goal, the process of taking action, and the final results as well.
Question 24:
What is your greatest goal in your career?
Answer:
Have a very specific goal of something you want to achieve in your career in mind, and be sure that it’s something the position clearly puts you in line to accomplish. Offer the goal as well as your plans to get there, and emphasize clear ways in which this position will be an opportunity to work toward the goal.
Question 25:
Tell me about a time when you achieved a goal.
Answer:
Start out with how you set the goal, and why you chose it. Then, take the interviewer through the process of outlining the goal, taking steps to achieve it, the outcome, and finally, how you felt after achieving it or the recognition you received. The most important part of this question includes the planning and implementation of strategies, so focus most of your time on explaining these aspects. However, the preliminary decisions and end results are also important, so make sure to include them as well.
Question 26:
What areas of your work would you still like to improve in? What are your plans to do this?
Answer:
While you may not want the interviewer to focus on things you could improve on, it’s important to be self-aware of your own growth opportunities. More importantly, you can impress an interviewer by having specific goals and actions outlined in order to facilitate your growth, even if your area of improvement is something as simple as increasing sales or finding new ways to create greater efficiency.
Question 27:
Tell me about your favorite book or newspaper.
Answer:
The interviewer will look at your answer to this question in order to determine your ability to analyze and review critically. Additionally, try to choose something that is on a topic related to your field or that embodies a theme important to your work, and be able to explain how it relates. Stay away from the controversial subjects matter, such as politics or religion.
Question 28:
If you could be rich or famous, which would you choose?
Answer:
This question speaks to your ability to think creatively, but your answer may also give great insight into your character. If you answer rich, your interviewer may interpret that you are self-confident and don’t seek approval from others and that you like to be rewarded for your work. If you choose famously, your interviewer may gather that you like to be well-known and to deal with people, and have the platform to deliver your message to others. Either way, it’s important to back up your answer with sound reasoning.
Question 29:
If you could trade places with anyone for a week, who would it be and why?
Answer:
This question is largely designed to test your ability to think on your feet, and to come up with a reasonable answer to an outside-the-box question. Whoever you choose, explain your S. answer in a logical manner, and offer specific professional reasons that led you to choose the individual.
Question 30:
What would you say if I told you that just from glancing over your resume, I can already see three spelling mistakes?
Answer:
Clearly, your resume should be absolutely spotless – and you should be confident that it is. If your interviewer tries to make you second-guess yourself here, remain calm and poised and assert with a polite smile that you would be quite surprised as you are positive that your resume is error-free.
Question 31:
Tell me about your worldview.
Answer:
This question is designed to offer insight into your personality, so be aware of how the interviewer will interpret your answer.
Speak openly and directly, and try to incorporate your own job skills into your outlook on life. For example, discuss your
beliefs on the ways that hard work and dedication can always bring success, or in how learning new things is one of life’s greatest gifts. It’s okay to expand into general life principles here, but try to keep your thoughts related to the professional field as well.
Question 32:
What is the biggest mistake someone could make in an interview?
Answer:
The biggest mistake that could be made in an interview is to be caught off guard! Make sure that you don’t commit whatever you answer here, and additionally be prepared for all questions. Other common mistakes include asking too early in the hiring process about job benefits, not having questions prepared when the interviewer asks if you have questions, arriving late, dressing casually or sloppily, or showing ignorance of the position.
Question 33:
If you won the $50m lotteries, what would you do with the money?
Answer:
While a question such as this may seem out of place in a job interview, it’s important to display your creative thinking and your ability to think on the spot. It’s also helpful if you choose something admirable, yet believable, to do with the money such as donate the first seventy percent to a charitable cause, and divide the remainder among gifts for friends, family, and of course, yourself.
Question 34:
Is there ever a time when honesty isn’t appropriate in the workplace?
Answer:
This may be a difficult question, but the only time that honesty isn’t appropriate in the workplace is perhaps when you’re feeling anger or another emotion that is best kept to yourself. If this is the case, explain simply that it is best to put some thoughts aside, and clarify that the process of keeping some thoughts quiet is often enough to smooth over any unsettled emotions, thus eliminating the problem.
35: If you could travel anywhere in the world, where would it – be?
Answer:
This question is meant to allow you to be creative – so go ahead s and stretch your thoughts to come up with a unique answer. However, be sure to keep your answer professionally-minded. For example, choose somewhere rich with culture or that would expose you to a new experience, rather than going on an. expensive cruise through the Bahamas.
Question 36:
What would I find in your refrigerator right now?
Answer:
An interviewer may ask a creative question such as this in order to discern your ability to answer unexpected questions calmly, or, to try to gain some insight into your personality. For example, candidates with a refrigerator full of junk food or \ take-out may be more likely to be under stress or have health issues, while a candidate with a balanced refrigerator full of nutritious staples may be more likely to lead a balanced mental life, as well.
Question 37:
If you could play any sport professionally, what would it be and what aspect draws you to it?
Answer:
Even if you don’t know much about professional sports, this question might be a great opportunity to highlight some of your greatest professional working skills. For example, you may choose to play professional basketball, because you admire the teamwork and coordination that goes into creating a solid play. Or, you may choose to play professional tennis, because you consider yourself to be a go-getter with a solid work ethic and great dedication to perfecting your craft. Explain your choice simply to the interviewer without elaborating on drawn-out sports metaphors, and be sure to point out specific areas or skills in which you excel.
Question 38:
Who were the presidential and vice-presidential candidates in the 2008 elections?
Answer:
This question, plain and simple, is intended as a gauge of your intelligence and awareness. If you miss this question, you may well fail the interview. Offer your response with a polite smile, because you understand that there are some individuals who probably miss this question.
Question 39:
Explain X task in a few short sentences as you would to a second-grader.
Answer:
An interviewer may ask you to break down a normal job task that you would complete in a manner that a child could understand, in part to test your knowledge of the task’s inner workings – but in larger part, to test your ability to explain a process in simple, basic terms. While you and your coworkers may be able to converse using highly technical language, being able to simplify a process is an important skill for any employee to have.
Question 40:
If you could compare yourself to any animal, what would it be?
Answer:
Many interviewers ask this question, and it’s not to determine which character traits you think you embody – instead, the interviewer wants to see that you can think outside the box and that you’re able to reason your way through any situation. Regardless of what animal you answer, be sure that you provide a thorough reason for your choice.
Question 41:
Who is your hero?
Answer:
Your hero may be your mother or father, an old professor, someone successful in your field, or perhaps even Wonder Woman – but keep your reasoning for your chosen profession, and be prepared to offer a logical train of thought. Choose someone who embodies values that are important in your chosen career field, and answer the question with a smile and a sense of passion.
Question 42:
Who would play you in the movie about your life?
Answer:
As with many creative questions that challenge an interviewee to think outside the box, the answer to this question is not as important as how you answer it. Choose a professional, and relatively non-controversial actor or actress, and then be prepared to offer specific reasoning for your choice, employing important skills or traits you possess.
Question 43:
Name five people, alive or dead, that would be at your ideal dinner party.
Answer:
Smile and sound excited at the opportunity to think outside the box when asked this question, even if it seems to come from left field. Choose dynamic, inspiring individuals who you could truly learn from, and explain what each of them would have to offer to the conversation. Don’t forget to include yourself, and to talk about what you would bring to the conversation as well!
Question 44:
What is customer service?
Answer:
Customer service can be many things – and the most important consideration in this question is that you have a creative
answer. Demonstrate your ability to think outside the box by offering a confident answer that goes past a basic definition, and that shows you have truly considered your own individual view of what it means to take care of your customers. The thoughtful consideration you hold for customers will speak for, itself.
Question 45:
Tell me about a time when you went out of your way for a customer.
Answer:
It’s important that you offer an example of a time you truly went out of your way – be careful not to confuse something that felt like a big effort on your part, with something your employer would expect you to do anyway. Offer an example of the customer’s problems, what you did to solve them, and the way the customer responded after you took care of the situation.
Question 46:
How do you gain confidence from customers?
Answer:
This is a very open-ended question that allows you to show your customer service skills to the interviewer. There are many possible answers, and it is best to choose something that you’ve had a great experience with, such as “by handling situations with transparency,” “offering rewards,” or “focusing on great communication.” Offer specific examples of successes you’ve had.
Question 47:
Tell me about a time when a customer was upset or agitated – how did you handle the situation?
Answer:
Similarly to handling a dispute with another employee, the most important part to answering this question is to first set up the scenario, offer a step-by-step guide to your particular conflict resolution style, and end by describing the way the conflict was resolved. Be sure that in answering questions about your own conflict resolution style, that you emphasize the importance of open communication and understanding from both parties, as well as a willingness to reach a compromise or other solution.
Question 48:
When can you make an exception for a customer?
Answer:
Exceptions for customers can generally be made when in accordance with company policy or when directed by a supervisor. Display an understanding of the types of situations in which an exception should be considered, such as when a customer has endured a particular hardship, had a complication with an order, or at a request.
Question 49:
What would you do in a situation where you were needed by both a customer and your boss?
Answer:
While both your customer and your boss have different needs of you and are very important to your success as a worker, it is always best to try to attend to your customer first – however, the key is explaining to your boss why you are needed urgently. by the customer, and then to assure your boss that you will attend to his or her needs as soon as possible (unless it’s absolutely an urgent matter).
Question 50:
What is the most important aspect of customer service?
Answer:
While many people would simply state that customer satisfaction is the most important aspect of customer service, it’s important to be able to elaborate on other important techniques in customer service situations. Explain why customer service is such a key part of business, and be sure to expand on the aspect that you deem to be the most important in a way that is reasoned and well-thought-out.
Question 51:
Is it best to create low or high expectations for a customer?
Answer:
You may answer this question either way (after, of course, determining that the company does not have a clear opinion on the matter). However, no matter which way you answer the question, you must display a thorough thought process and very clear reasoning for the option you chose. Offer pros and cons of each, and include the ultimate point that tips the scale in favor of your chosen answer.
And Finally Good Luck!