Python Program for Multiplication of Two Matrices | How do you do Matrix Multiplication in Python?
Are you a job seeker and trying to find simple java programs for Interview? This would be the right choice for you, just tap on the link and start preparing the java programs covered to crack the interview.
Looking across the web for guidance on Multiplication of Two Matrices in Python? Before you begin your learning on Matrix Multiplication of Two Matrices know what is meant by a Matrix and what does Matrix Multiplication in actual means. This tutorial is going to be extremely helpful for you as it assists you completely on How to Multiply Two Matrices in Python using different methods like nested loops, nested list comprehension, etc. Furthermore, we have written simple python programs for multiplying two matrices clearly.
- What is a Matrix?
- What is Matrix Multiplication?
- Simple Python Program for Matrix Multiplication
- Method #1: Using Nested Loops in Python
- Method #2: Matrix Multiplication List Comprehension Python
- Method #3: Using Nested Loops in C++
- How to Multiply Two Matrices in Python using Numpy?
What is a Matrix?
A matrix is a rectangular sequence of numbers divided into columns and rows. A matrix element or entry is a number that appears in a matrix.
Example:
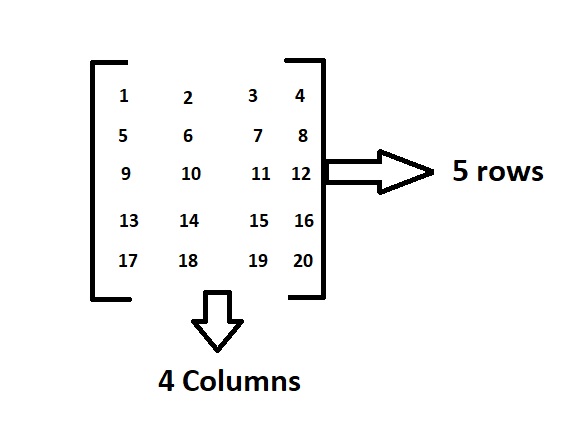
Above is the matrix which contains 5 rows and 4 columns and having elements from 1 to 20.
In this order, the dimensions of a matrix indicate the number of rows and columns.
Here as there are 5 rows and 4 columns it is called a 5*4 matrix.
What is Matrix Multiplication?
Matrix multiplication is only possible if the second matrix’s column equals the first matrix’s rows. A matrix can be represented in Python as a nested list ( a list inside a list ).
Examples for Matrix Multiplication:
Example 1:
Input:
Matrix 1 = [ 1 -8 7 ]
[ 0 2 5 ]
[ 1 6 2 ]
Matrix 2 = [ 5 2 -6 ]
[ 1 8 9 ]
[ 3 5 7 ]Output:
printing the matrix A : 1 -8 7 0 2 5 1 6 2 printing the matrix B : 5 2 -6 1 8 9 3 5 7 Printing the product of matrices : 18 -27 -29 17 41 53 17 60 62
Example 2:
Input:
Matrix 1 = 1 2 3
-5 8 7
6 4 5
Matrix 2 = 2 7 9
0 -8 5
6 -5 2Output:
Enter the number of rows and columns of the first matrix3 3 Enter the number of rows and columns of the second matrix3 3 Enter element A11 = 1 Enter element A12 = 2 Enter element A13 = 3 Enter element A21 = -5 Enter element A22 = 8 Enter element A23 = 7 Enter element A31 = 6 Enter element A32 = 4 Enter element A33 = 5 Enter elements of 2nd matrix: Enter element B11 = 2 Enter element B12 = 7 Enter element B13 = 9 Enter element B21 = 0 Enter element B22 = -8 Enter element B23 = 5 Enter element B31 = 6 Enter element B32 = -5 Enter element B33 = 2 printing the matrix A 1 2 3 -5 8 7 6 4 5 printing the matrix B 2 7 9 0 -8 5 6 -5 2 Print the product of two matrices A and B 20 -24 25 32 -134 9 42 -15 84
Given two matrices, the task is to write a program in Python and C++ to multiply the two matrices.
Simple Python Program for Matrix Multiplication
Method #1: Using Nested Loops in Python
A matrix can be implemented as a nested list in Python (list inside a list).
Each element can be thought of as a row in the matrix.
X[0] can be used to choose the first row. Furthermore, the element in the first row, the first column can be chosen as X[0][0].
The multiplication of two matrices X and Y is defined if the number of columns in X equals the number of rows in Y.
Here we give the matrix input as static.
XY is defined and has the dimension n x l if X is a n x m matrix and Y is a m x l matrix (but YX is not defined). In Python, there are a few different approaches to implement matrix multiplication.
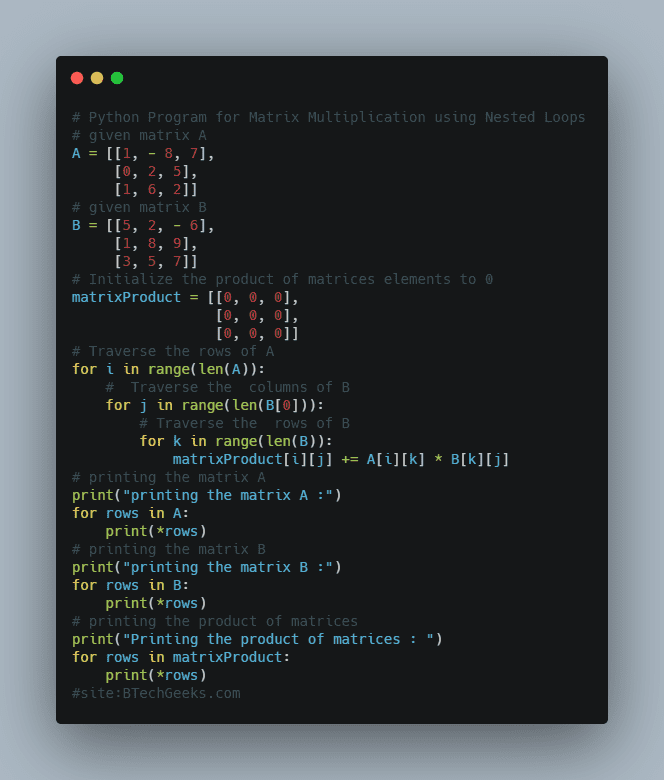
Below is the implementation:
# given matrix A
A = [[1, - 8, 7],
[0, 2, 5],
[1, 6, 2]]
# given matrix B
B = [[5, 2, - 6],
[1, 8, 9],
[3, 5, 7]]
# Initialize the product of matrices elements to 0
matrixProduct = [[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]]
# Traverse the rows of A
for i in range(len(A)):
# Traverse the columns of B
for j in range(len(B[0])):
# Traverse the rows of B
for k in range(len(B)):
matrixProduct[i][j] += A[i][k] * B[k][j]
# printing the matrix A
print("printing the matrix A :")
for rows in A:
print(*rows)
# printing the matrix B
print("printing the matrix B :")
for rows in B:
print(*rows)
# printing the product of matrices
print("Printing the product of matrices : ")
for rows in matrixProduct:
print(*rows)
Output:
printing the matrix A : 1 -8 7 0 2 5 1 6 2 printing the matrix B : 5 2 -6 1 8 9 3 5 7 Printing the product of matrices : 18 -27 -29 17 41 53 17 60 62
Explanation:
To go through each row and column in our program, we used nested for loops. In the end, we add up the sum of the items.
This technique is simple, but it becomes computationally expensive as the order of the matrix increases.
We recommend NumPy for larger matrix operations because it is several (in the order of 1000) times faster than the above code.
Method #2: Matrix Multiplication List Comprehension Python
This program produces the same results as the previous one. To understand the preceding code, we must first know the built-in method zip() and how to unpack an argument list with the * operator.
To loop through each element in the matrix, we utilized nested list comprehension. At first glance, the code appears to be complicated and difficult to understand. However, once you’ve learned list comprehensions, you won’t want to go back to nested loops.
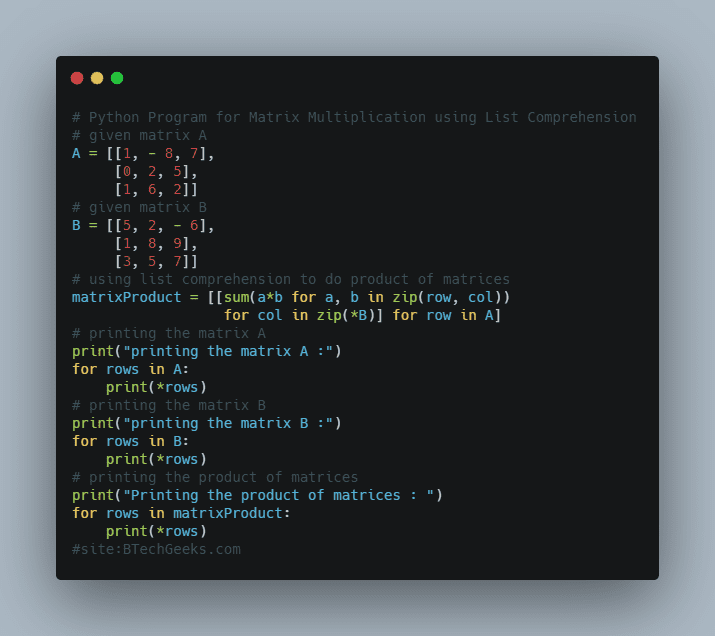
Below is the implementation:
# given matrix A
A = [[1, - 8, 7],
[0, 2, 5],
[1, 6, 2]]
# given matrix B
B = [[5, 2, - 6],
[1, 8, 9],
[3, 5, 7]]
# using list comprehension to do product of matrices
matrixProduct = [[sum(a*b for a, b in zip(row, col))
for col in zip(*B)] for row in A]
# printing the matrix A
print("printing the matrix A :")
for rows in A:
print(*rows)
# printing the matrix B
print("printing the matrix B :")
for rows in B:
print(*rows)
# printing the product of matrices
print("Printing the product of matrices : ")
for rows in matrixProduct:
print(*rows)
Output:
printing the matrix A : 1 -8 7 0 2 5 1 6 2 printing the matrix B : 5 2 -6 1 8 9 3 5 7 Printing the product of matrices : 18 -27 -29 17 41 53 17 60 62
Method #3: Using Nested Loops in C++
We used nesting loops in this program to iterate through and row and column. In order to multiply two matrices, we will do the multiplication of matrices as below
Let us take dynamic input in this case.
Below is the implementation:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int A[100][100], B[100][100], product[100][100], row1,
col1, row2, col2, i, j, k;
cout << "Enter the number of rows and columns of the "
"first matrix";
cin >> row1 >> col1;
cout << "Enter the number of rows and columns of the "
"second matrix";
cin >> row2 >> col2;
// Initializing matrix A with the user defined values
for (i = 0; i < row1; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < col1; ++j) {
cout << "Enter element A" << i + 1 << j + 1
<< " = ";
cin >> A[i][j];
}
// Initializing matrix B with the user defined values
cout << endl
<< "Enter elements of 2nd matrix: " << endl;
for (i = 0; i < row2; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < col2; ++j) {
cout << "Enter element B" << i + 1 << j + 1
<< " = ";
cin >> B[i][j];
}
// Initializing the resultant product matrix with 0 to
// all elements
for (i = 0; i < row1; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < col2; ++j) {
product[i][j] = 0;
}
// Calculating the product of two matrices A and B
for (i = 0; i < row1; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < col2; ++j)
for (k = 0; k < col1; ++k) {
product[i][j] += A[i][k] * B[k][j];
}
// printing matrix A
cout << endl << " printing the matrix A" << endl;
for (i = 0; i < row1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < col1; ++j) {
cout << A[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// printing matrix B
cout << endl << " printing the matrix B" << endl;
for (i = 0; i < row2; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < col2; ++j) {
cout << B[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Print the product of two matrices A and B
cout << "Print the product of two matrices A and B"
<< endl;
for (i = 0; i < row1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < col2; ++j) {
cout << product[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}Output:
Enter the number of rows and columns of the first matrix3 3 Enter the number of rows and columns of the second matrix3 3 Enter element A11 = 1 Enter element A12 = 2 Enter element A13 = 3 Enter element A21 = -5 Enter element A22 = 8 Enter element A23 = 7 Enter element A31 = 6 Enter element A32 = 4 Enter element A33 = 5 Enter elements of 2nd matrix: Enter element B11 = 2 Enter element B12 = 7 Enter element B13 = 9 Enter element B21 = 0 Enter element B22 = -8 Enter element B23 = 5 Enter element B31 = 6 Enter element B32 = -5 Enter element B33 = 2 printing the matrix A 1 2 3 -5 8 7 6 4 5 printing the matrix B 2 7 9 0 -8 5 6 -5 2 Print the product of two matrices A and B 20 -24 25 32 -134 9 42 -15 84
How to Multiply Two Matrices in Python using Numpy?
import numpy as np C = np.array([[3, 6, 7], [5, -3, 0]]) D = np.array([[1, 1], [2, 1], [3, -3]]) E = C.dot(D) print(E) '''
Output:
[[ 36 -12] [ -1 2]]
Explore more instances related to python concepts from Python Programming Examples Guide and get promoted from beginner to professional programmer level in Python Programming Language.
Related Programs:
- program for addition of two matrices in python cpp
- python program to find the lcm of two numbers
- python program to find whether a number is a power of two
- python program to find the product of two numbers using recursion
- python program to find the lcm of two numbers using recursion
- python program to find the minimum difference between the index of two given elements present in an array
- python program to find the factorial of a number