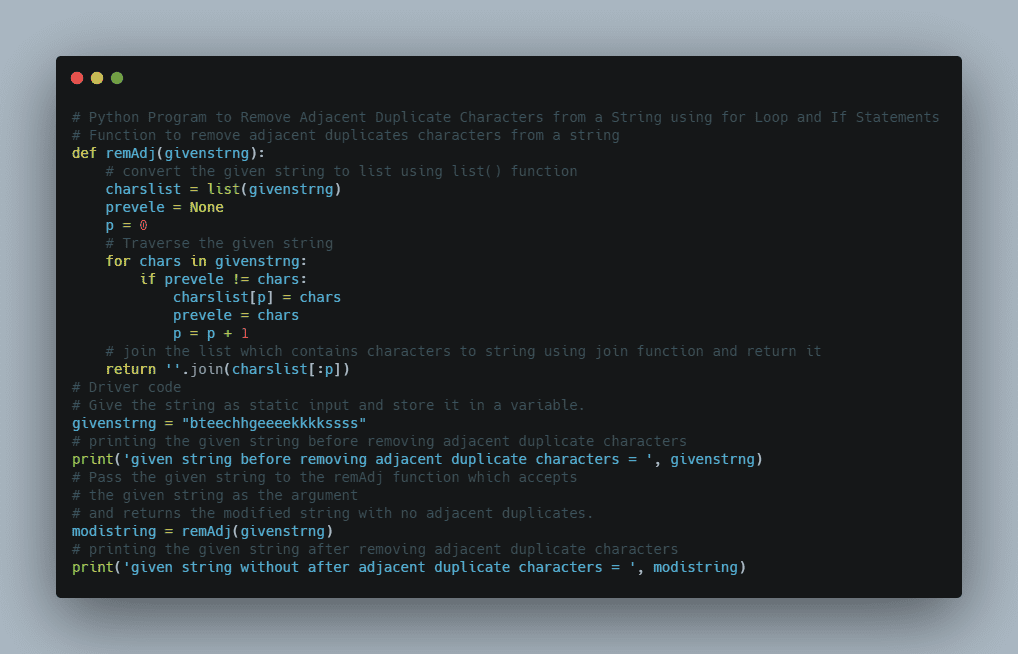
Print all Integers that Aren’t Divisible by Either 2 or 3 and Lie between 1 and 50 in C++ and Python
In the previous article, we have discussed about Allocating and deallocating 2D arrays dynamically in C++. Let us learn how to Print all Integers that Aren’t Divisible by Either 2 or 3 and Lie between 1 and 50 in C++ Program.
The task is to print all the numbers from 1 to 50 which are not divisible by 2 or 3 in C++ and Python.
Sample Output:
The numbers from 1 to 50 which are not divisible by 2 and 3 are: Number = 1 Number = 5 Number = 7 Number = 11 Number = 13 Number = 17 Number = 19 Number = 23 Number = 25 Number = 29 Number = 31 Number = 35 Number = 37 Number = 41 Number = 43 Number = 47 Number = 49
Print all Integers that Aren’t Divisible by Either 2 or 3 and Lie between 1 and 50 in C++ and Python
Grab the opportunity to learn all effective java programming language concepts from basic to advance levels by practicing these Java Program Examples with Output
There are several ways to print all the numbers from 1 to 50 which are not divisible by 2 or 3 some of them are:
Method #1: Using for loop in Python
Approach:
- Use a for loop and a range() function which iterates from 1 to 50.
- Then, using an if statement, determine whether the integer is not divisible by both 2 and 3.
- If the number is not divisible by 2 and 3 then print it.
- Exit of program
Below is the implementation:
# Use a for loop and a range() function which iterates from 1 to 50.
print("The numbers from 1 to 50 which are not divisible by 2 and 3 are:")
for numb in range(1, 51):
# Then, using an if statement, determine whether the integer is
# not divisible by both 2 and 3.
if(numb % 2 != 0 and numb % 3 != 0):
# If the number is not divisible by 2 and 3 then print it.
print("Number = ", numb)
Output:
The numbers from 1 to 50 which are not divisible by 2 and 3 are: Number = 1 Number = 5 Number = 7 Number = 11 Number = 13 Number = 17 Number = 19 Number = 23 Number = 25 Number = 29 Number = 31 Number = 35 Number = 37 Number = 41 Number = 43 Number = 47 Number = 49
Method #2: Using for loop in C++
Approach:
- Use for loop in Which starts from 1 and ends at 50 using the
- syntax : for (numb=1;numb<=50;numb++)
- Then, using an if statement, determine whether the integer is not divisible by both 2 and 3.
- If the number is not divisible by 2 and 3 then print it.
- Exit of program
Below is the implementation:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Use for loop in Which starts from 1 and ends at 50
// using the syntax : for (numb=1;numb<=50;numb++)
cout << "The numbers from 1 to 50 which are not "
"divisible by 2 and 3 are:"
<< endl;
for (int numb = 1; numb <= 50; numb++) {
// Then, using an if statement determine whether the
// integer is not divisible by both 2 and 3.
if (numb % 2 != 0 && numb % 3 != 0) {
// If the number is not divisible by 2 and 3
// then print it.
cout << "Number = " << numb << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}Output:
The numbers from 1 to 50 which are not divisible by 2 and 3 are: Number = 1 Number = 5 Number = 7 Number = 11 Number = 13 Number = 17 Number = 19 Number = 23 Number = 25 Number = 29 Number = 31 Number = 35 Number = 37 Number = 41 Number = 43 Number = 47 Number = 49
Method #3: Using while loop in Python
Approach:
- Take a variable say tempo which stores the lower limit (in this case it is 1)
- Using while loop iterate from 1 to 51 by using the condition tempo <=50
- Then, using an if statement, determine whether the integer is not divisible by both 2 and 3.
- If the number is not divisible by 2 and 3 then print it.
- Increment the value of tempo by 1
- Exit of program
Below is the implementation:
# Use a for loop and a range() function which iterates from 1 to 50.
print("The numbers from 1 to 50 which are not divisible by 2 and 3 are:")
# Take a integer variable say tempo which stores the lower limit (in this case it is 1)
tempo = 1
# Using while loop iterate from 1 to 51 by using the condition tempo <=50
while(tempo <= 50):
# Then, using an if statement, determine whether the integer is
# not divisible by both 2 and 3.
if(tempo % 2 != 0 and tempo % 3 != 0):
# If the number is not divisible by 2 and 3 then print it.
print('Number =', tempo)
# Increment the value of tempo by 1
tempo = tempo+1
Output:
The numbers from 1 to 50 which are not divisible by 2 and 3 are: Number = 1 Number = 5 Number = 7 Number = 11 Number = 13 Number = 17 Number = 19 Number = 23 Number = 25 Number = 29 Number = 31 Number = 35 Number = 37 Number = 41 Number = 43 Number = 47 Number = 49
Method #4: Using while loop in C++
Approach:
- Take a integer variable say tempo which stores the lower limit (in this case it is 1)
- Using while loop iterate from 1 to 51 by using the condition tempo <=50
- Then, using an if statement, determine whether the integer is not divisible by both 2 and 3.
- If the number is not divisible by 2 and 3 then print it.
- Increment the value of tempo by 1
- Exit of program
Below is the implementation:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Use for loop in Which starts from 1 and ends at 50
// using the syntax : for (numb=1;numb<=50;numb++)
cout << "The numbers from 1 to 50 which are not "
"divisible by 2 and 3 are:"
<< endl;
// Take a integer variable say tempo which stores the
// lower limit (in this case it is 1)
int tempo = 1;
// Using while loop iterate from 1 to 51 by using the
// condition tempo <=50
while (tempo <= 50) {
// Then, using an if statement determine whether the
// integer is not divisible by both 2 and 3.
if (tempo % 2 != 0 && tempo % 3 != 0) {
// If the number is not divisible by 2 and 3
// then print it.
cout << "Number = " << tempo << endl;
}
// Increment the value of tempo by 1
tempo = tempo + 1;
}
return 0;
}Output:
The numbers from 1 to 50 which are not divisible by 2 and 3 are: Number = 1 Number = 5 Number = 7 Number = 11 Number = 13 Number = 17 Number = 19 Number = 23 Number = 25 Number = 29 Number = 31 Number = 35 Number = 37 Number = 41 Number = 43 Number = 47 Number = 49
Related Programs:
- Python Program to Form an Integer that has the Number of Digits at Ten’s Place and
the Least Significant Digit of the Entered Integer at One’s Place - Python Program to Find Those Numbers which are Divisible by 7 and Multiple of 5 in a Given Range of Numbers
- Python Program to Compute Prime Factors of an Integer
- Python Program to Find the Smallest Divisor of an Integer
- Python Program to Make a Simple Calculator