In this tutorial, we will learn how to find the indexes of a row and column numbers using pandas in a dataframe. By learning from this tutorial, you can easily get a good grip on how to get row names in Pandas dataframe. Also, there is a possibility to learn about the Python Pandas Index.get_loc() function along with syntax, parameters, and a sample example program.
- Pandas Index.get_loc() Function in Python
- Syntax
- Parameters
- Return Value
- Example using Index.get_loc() function
- Creating a Dataframe in Python
- Find all indexes of an item in pandas dataframe
- How did it work?
- Find index positions of multiple elements in the DataFrame
Pandas Index.get_loc() Function in Python
PandasIndex.get_loc()function results integer location, slice, or boolean mask for the requested label. The function acts with both sorted as well as unsorted Indexes. It gives various options if the passed value is not present in the Index.
Syntax:
Index.get_loc(key, method=None, tolerance=None)
Parameters:
- key: label
- method: {None, ‘pad’/’ffill’, ‘backfill’/’bfill’, ‘nearest’}, optional
- default: exact matches only.
- pad / ffill: If not having the exact match, find the PREVIOUS index value.
- backfill / bfill: Utilize NEXT index value if no exact match
- nearest: Make use of the NEAREST index value if no exact match. Tied distances are broken by preferring the larger index value.
Return Value:
loc : int if unique index, slice if monotonic index, else mask
Example using Index.get_loc() function:
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Index
idx = pd.Index(['Labrador', 'Beagle', 'Labrador',
'Lhasa', 'Husky', 'Beagle'])
# Print the Index
idx
Also View:
- Python: Add column to dataframe in Pandas ( based on other column or list or default value)
- Pandas: Delete last column of dataframe in python
Creating a Dataframe in Python
The initial step is creating a dataframe.
Code:
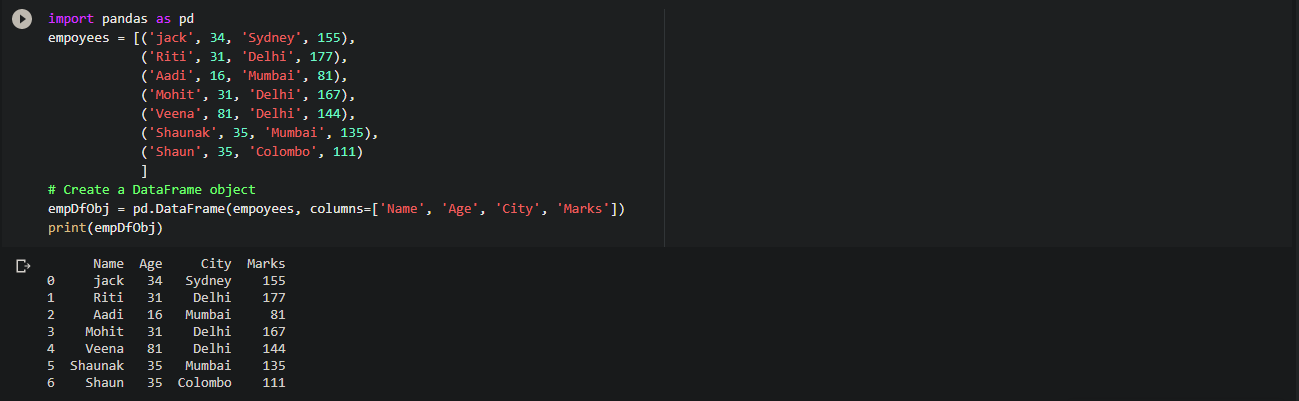
# List of Tuples
empoyees = [('jack', 34, 'Sydney', 155),
('Riti', 31, 'Delhi', 177),
('Aadi', 16, 'Mumbai', 81),
('Mohit', 31, 'Delhi', 167),
('Veena', 81, 'Delhi', 144),
('Shaunak', 35, 'Mumbai', 135),
('Shaun', 35, 'Colombo', 111)
]
# Create a DataFrame object
empDfObj = pd.DataFrame(empoyees, columns=['Name', 'Age', 'City', 'Marks'])
print(empDfObj)
Output:
Now, we want to find the location where the value ’81’ exists.
(4, 'Age') (2, 'Marks')
We can see that value ’81’ exists at two different places in the data frame.
- At row index 4 & column “Age”
- At row index 2 & column “Marks”
Now, we will proceed to get the result of this.
Find all indexes of an item in pandas dataframe
Dataframe object and the value as an argument is accepted by the function we have created.
It returns the list of index positions at all occurrences.
Code:
def getIndexes(dfObj, value):
''' Get index positions of value in dataframe i.e. dfObj.'''
listOfPos = list()
# Get bool dataframe with True at positions where the given value exists
result = dfObj.isin([value])
# Get list of columns that contains the value
seriesObj = result.any()
columnNames = list(seriesObj[seriesObj == True].index)
# Iterate over list of columns and fetch the rows indexes where value exists
for col in columnNames:
rows = list(result[col][result[col] == True].index)
for row in rows:
listOfPos.append((row, col))
# Return a list of tuples indicating the positions of value in the dataframe
return listOfPos
Output:
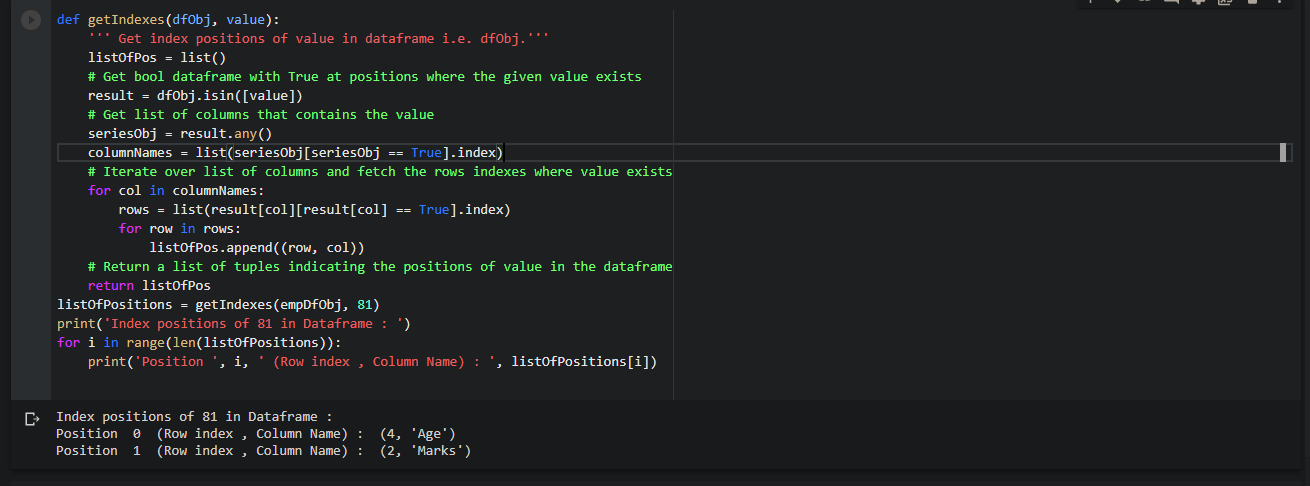
We got the exact row and column names of all the locations where the value ’81’ exists.
We will see what happened inside the getIndexes function.
How did it work?
Now, we will learn step by step process on what happened inside the getIndexes() function.
Step 1: Get bool dataframe with True at positions where the value is 81 in the dataframe using pandas.DataFrame.isin()
DataFrame.isin(self, values)
This isin() function accepts a value and returns a bool dataframe. The original size and the bool data frame size is the same. When the given value exists, it contains True otherwise False.
We will see the bool dataframe where the value is ’81’.
# Get bool dataframe with True at positions where value is 81
result = empDfObj.isin([81])
print('Bool Dataframe representing existence of value 81 as True')
print(result)
Output:
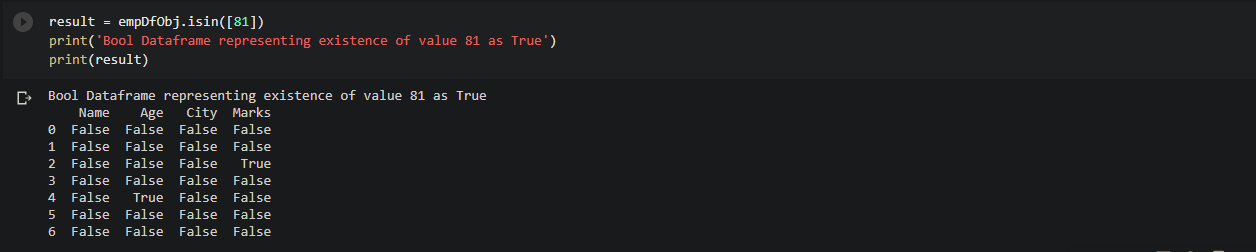
It is of the same size as empDfObj. As 81 exists at 2 places inside the dataframe, so this bool dataframe contains True at only those two places. In all other places, it contains False.
Step 2: Get the list of columns that contains the value
We will get the name of the columns that contain the value ’81’.We will achieve this by fetching names in a column in the bool dataframe which contains True value.
Code:
# Get list of columns that contains the value i.e. 81
seriesObj = result.any()
columnNames = list(seriesObj[seriesObj == True].index)
print('Names of columns which contains 81:', columnNames)
Output:
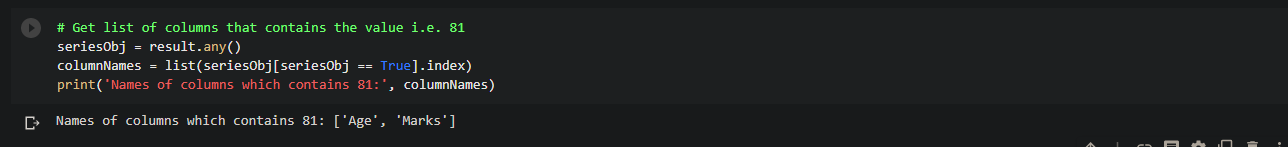
Step 3: Iterate over selected columns and fetch the indexes of the rows which contains the value
We will iterate over each selected column and for each column, we will find the row which contains the True value.
Now these combinations of column names and row indexes where True exists are the index positions of 81 in the dataframe i.e.
Code:
# Iterate over each column and fetch the rows number where
for col in columnNames:
rows = list(result[col][result[col] == True].index)
for row in rows:
print('Index : ', row, ' Col : ', col)
Output:

Now it is clear that this is the way the getIndexes() function was working and finding the exact index positions of the given value & store each position as (row, column) tuple. In the end, it returns a list of tuples representing its index positions in the dataframe.
Find index positions of multiple elements in the DataFrame
Suppose we have multiple elements,
[81, 'Delhi', 'abc']
Now we want to find index positions of all these elements in our dataframe empDfObj, like this,
81 : [(4, 'Age'), (2, 'Marks')] Delhi : [(1, 'City'), (3, 'City'), (4, 'City')] abc : []
Let’s use the getIndexes() and dictionary comprehension to find the indexes of all occurrences of multiple elements in the dataframe empDfObj.
listOfElems = [81, 'Delhi', 'abc']
# Use dict comprhension to club index positions of multiple elements in dataframe
dictOfPos = {elem: getIndexes(empDfObj, elem) for elem in listOfElems}
print('Position of given elements in Dataframe are : ')
for key, value in dictOfPos.items():
print(key, ' : ', value)
Output:
dictOfPos is a dictionary of elements and their index positions in the dataframe. As ‘abc‘ doesn’t exist in the dataframe, therefore, its list is empty in dictionary dictOfPos.
Hope this article was understandable and easy for you!
Want to expert in the python programming language? Exploring Python Data Analysis using Pandas tutorial changes your knowledge from basic to advance level in python concepts.
Read more Articles on Python Data Analysis Using Padas – Find Elements in a Dataframe
- Check if a value exists in a DataFrame using in & not in operator | isin()
- Find & Drop duplicate columns in a DataFrame
- Check if a DataFrame is empty in Python
- Find duplicate rows in a Dataframe based on all or selected columns using DataFrame.duplicated() in Python
- Find maximum values & position in columns or rows of a Dataframe
