Python Program to Print All Permutations of a String in Lexicographic Order without Recursion
Strings in Python:
Strings are simple text in programming, which might be individual letters, words, phrases, or whole sentences. Python strings have powerful text-processing capabilities, such as searching and replacing characters, cutting characters, and changing case. Empty strings are written as two quotations separated by a space. Single or double quotation marks may be used. Three quote characters can be used to easily build multi-line strings.
Given a string ,the task is to print all the permutations of the given string in lexicographic order without using recursion in Python.
Examples:
Example1:
Input:
given string ='hug'
Output:
printing all [ hug ] permutations : hug ugh uhg ghu guh hgu
Example2:
Input:
given string ='tork'
Output:
printing all [ tork ] permutations : tork trko trok kort kotr krot krto ktor ktro okrt oktr orkt ortk otkr otrk rkot rkto rokt rotk rtko rtok tkor tkro tokr
Program to Print All Permutations of a String in Lexicographic Order without Recursion
Below are the ways to Print All string permutations without recursion in lexicographic order:
Have you mastered basic programming topics of java and looking forward to mastering advanced topics in a java programming language? Go with these ultimate Advanced java programs examples with output & achieve your goal in improving java coding skills.
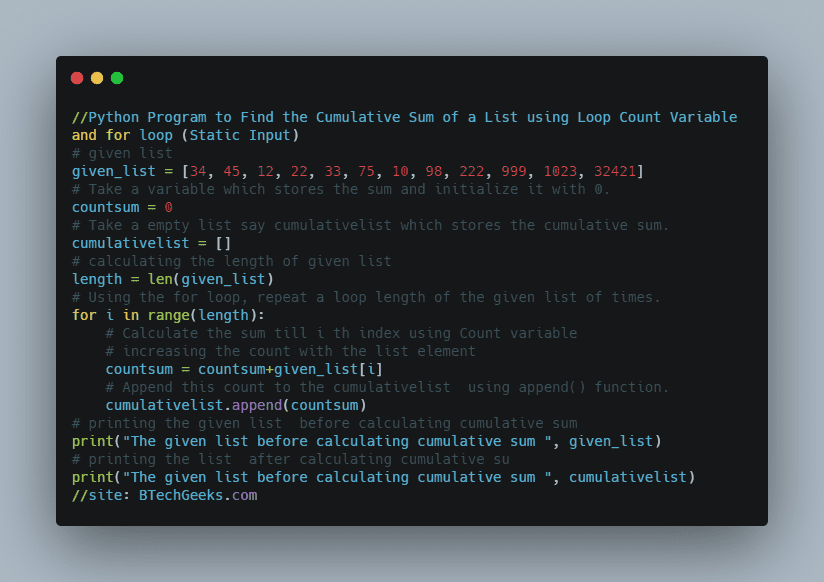
1)Using for and while Loops(Static Input)
Approach:
- Give the string as static input.
- The algorithm works by first generating a loop that will run n! times, where n is the length of the string.
- Each loop iteration produces the string and looks for its next variant to print in the following iteration.
- The following is the next higher permutation.
- If we call our sequence seq, we identify the least index p such that all entries in seq[p…end] are in decreasing order.
- If seq[p…end] represents the whole sequence, i.e. p == 0, then seq is the highest permutation. So we simply reverse the entire string to find the shortest permutation, which we regard to be the next permutation.
- If p > 0, we reverse seq[p…end].
Below is the implementation:
from math import factorial
def printPermutationsLexico(string):
# In lexicographic sequence, print all permutations of string s.
stringseq = list(string)
# There will be n! permutations where n = len (seq).
for t in range(factorial(len(stringseq))):
# print permutation by joining all the characters using join() function
print(''.join(stringseq))
# Find p such that seq[per:] is the longest sequence with lexicographic
# elements in decreasing order.
per = len(stringseq) - 1
while per > 0 and stringseq[per - 1] > stringseq[per]:
per -= 1
# reverse the stringsequence from per to end using reversed function
stringseq[per:] = reversed(stringseq[per:])
if per > 0:
# Find q such that seq[q] is the smallest element in seq[per:] and seq[q] is greater
# than seq[p - 1].Find q such that seq[q] is the smallest
# element in seq[per:] and seq[q] is greater than seq[per - 1].
q = per
while stringseq[per - 1] > stringseq[q]:
q += 1
# swapping seq[per - 1] and seq[q]
stringseq[per - 1], stringseq[q] = stringseq[q], stringseq[per - 1]
# given string as static input
given_string = 'hug'
# printing all the perumutations
print('printing all [', given_string, '] permutations :')
# passing given string to printPermutationsLexico function
printPermutationsLexico(given_string)
Output:
printing all [ hug ] permutations : hug ugh uhg ghu guh hgu
Explanation:
- User must give string input as static .
- On the string, the method printPermutationsLexico is called.
- The function then prints the string’s permutations in lexicographic order.
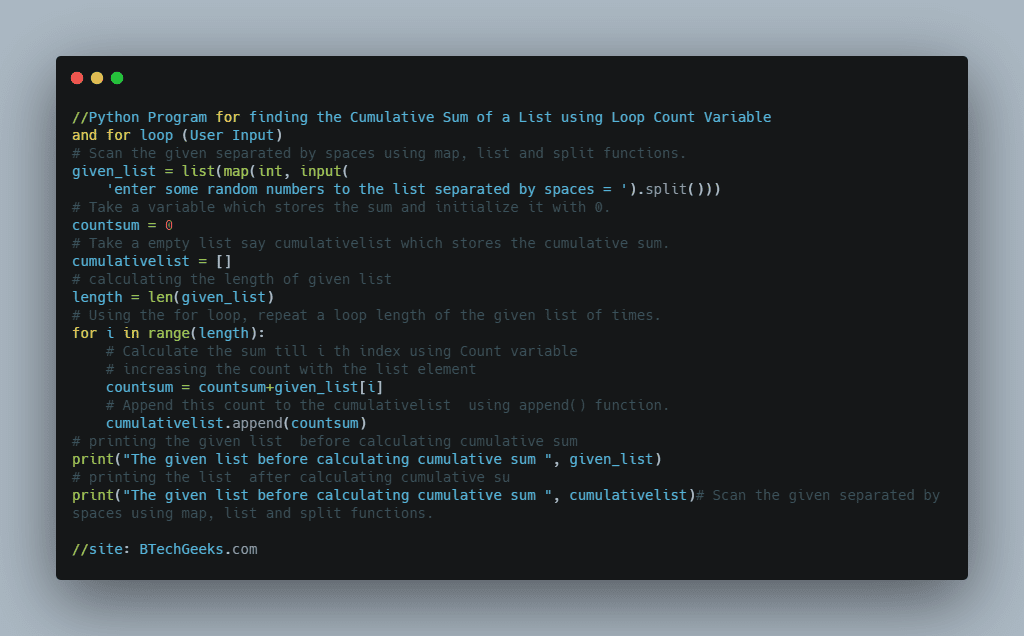
2)Using for and while Loops(User Input)
Approach:
- Enter some random string as user input using int(input()) function.
- The algorithm works by first generating a loop that will run n! times, where n is the length of the string.
- Each loop iteration produces the string and looks for its next variant to print in the following iteration.
- The following is the next higher permutation.
- If we call our sequence seq, we identify the least index p such that all entries in seq[p…end] are in decreasing order.
- If seq[p…end] represents the whole sequence, i.e. p == 0, then seq is the highest permutation. So we simply reverse the entire string to find the shortest permutation, which we regard to be the next permutation.
- If p > 0, we reverse seq[p…end].
Below is the implementation:
from math import factorial
def printPermutationsLexico(string):
# In lexicographic sequence, print all permutations of string s.
stringseq = list(string)
# There will be n! permutations where n = len (seq).
for t in range(factorial(len(stringseq))):
# print permutation by joining all the characters using join() function
print(''.join(stringseq))
# Find p such that seq[per:] is the longest sequence with lexicographic
# elements in decreasing order.
per = len(stringseq) - 1
while per > 0 and stringseq[per - 1] > stringseq[per]:
per -= 1
# reverse the stringsequence from per to end using reversed function
stringseq[per:] = reversed(stringseq[per:])
if per > 0:
# Find q such that seq[q] is the smallest element in seq[per:] and seq[q] is greater
# than seq[p - 1].Find q such that seq[q] is the smallest
# element in seq[per:] and seq[q] is greater than seq[per - 1].
q = per
while stringseq[per - 1] > stringseq[q]:
q += 1
# swapping seq[per - 1] and seq[q]
stringseq[per - 1], stringseq[q] = stringseq[q], stringseq[per - 1]
# Enter some random string as user input using int(input()) function.
given_string =input('Enter some random string = ')
# printing all the perumutations
print('printing all [', given_string, '] permutations :')
# passing given string to printPermutationsLexico function
printPermutationsLexico(given_string)
Output:
Enter some random string = epic printing all [ epic ] permutations : epic icep icpe iecp iepc ipce ipec pcei pcie peci peic pice piec ceip cepi ciep cipe cpei cpie ecip ecpi eicp eipc epci
Related Programs: