In the previous article, we have discussed Python Program to Print Odd Numbers in Given Range Using Recursion
Given a matrix and the task is to find the normal and trace of the given Matrix in Python.
What is a matrix:
A matrix is a rectangular sequence of numbers divided into columns and rows. A matrix element or entry is a number that appears in a matrix.
Example:
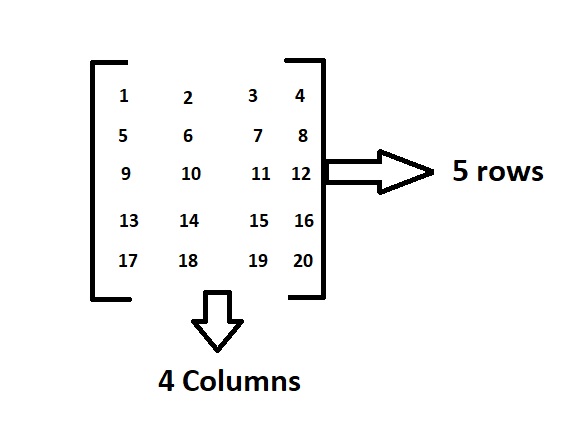
Above is the matrix which contains 5 rows and 4 columns and having elements from 1 to 20.
In this order, the dimensions of a matrix indicate the number of rows and columns.
Here as there are 5 rows and 4 columns it is called a 5*4 matrix.
Normal of a matrix:
The sum of squares is normal for all the matrix entries.
Trace of a matrix:
Trace is the sum of the Matrix’s diagonal parts.
Examples:
Example1:
Input:
Given Matix :
2 6 4
8 5 3
1 6 8
Output:
The trace value of the given matrix is : 15
The normal value of the given matrix is : 6.557438524302
Example2:
Input:
Given Matix :
1 2 3 4
7 5 8 6
9 4 2 5
1 1 1 1
Output:
The trace value of the given matrix is : 9
The normal value of the given matrix is : 7.745966692414834
Program to find the Normal and Trace of a Matrix in Python
Below are the ways to find the normal and trace of the given Matrix in Python:
Approach:
- Import the math module using the import keyword.
- Give the matrix as static input and store it in a variable.
- Calculate the number of rows of the given matrix by calculating the length of the nested list using the len() function and store it in a variable mtrxrows.
- Calculate the number of columns of the given matrix by calculating the length of the first list in the nested list using the len() function and store it in a variable mtrxcolums.
- Take a variable say mtrxtrace which stores the trace of the given matrix and initialize its value to 0.
- Take a variable say mtrxsum which stores the sum of all elements of the matrix and initialize its value to 0.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of columns using another Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
- Check if the parent loop iterator value is equal to the inner loop iterator value using the if conditional statement(This is whether the element is diagonal element or not)
- If it is true then add this value to mtrxtrace.
- After the if conditional statement, Add the gvnmatrix[n][m] to the above-initialized mtrxsum and store it in the same variable mtrxsum.
- After the end of two loops calculate the square root of the mtrxsum value using the sqrt() function and store this result in mtrxnormal variable.
- Print the value of mtrxtrace which gives the value of the trace of the given matrix.
- Print the value of mtrxnormal which gives the value of the normal of the given matrix.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import the math module using the import keyword.
import math
# Give the matrix as static input and store it in a variable.
mtrx = [[2, 6, 4], [8, 5, 3], [1, 6, 8]]
# Calculate the number of rows of the given matrix by
# calculating the length of the nested list using the len() function
# and store it in a variable mtrxrows.
mtrxrows = len(mtrx)
# Calculate the number of columns of the given matrix by
# calculating the length of the first list in the nested list
# using the len() function and store it in a variable mtrxcols.
mtrxcols = len(mtrx[0])
# Take a variable say mtrxtrace which stores the trace of the given matrix
# and initialize its value to 0.
mtrxtrace = 0
# Take a variable say mtrxsum which stores the sum of all elements of the matrix
# and initialize its value to 0.
mtrxsum = 0
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of columns using another
# Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
for m in range(mtrxcols):
# Check if the parent loop iterator value is equal to the inner loop iterator value
# using the if conditional statement
# (This is whether the element is diagonal element or not)
if(n == m):
# If it is true then add this value to mtrxtrace.
mtrxtrace = mtrxtrace+mtrx[n][m]
# After the if conditional statement,
# Add the gvnmatrix[n][m] to the above-initialized mtrxsum
# and store it in the same variable mtrxsum.
mtrxsum = mtrxsum+mtrx[n][m]
# After the end of two loops calculate the square root of the mtrxsum value
# using the sqrt() function
# and store this result in mtrxnormal variable.
mtrxnormal = math.sqrt(mtrxsum)
# Print the value of mtrxtrace which gives the value of the trace of the given matrix.
print('The trace value of the given matrix is :', mtrxtrace)
# Print the value of mtrxnormal which gives the value of the normal of the given matrix.
print('The normal value of the given matrix is :', mtrxnormal)
Output:
The trace value of the given matrix is : 15
The normal value of the given matrix is : 6.557438524302
Approach:
- Import the math module using the import keyword.
- Give the number of rows of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function and store it in a variable.
- Give the number of columns of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function and store it in another variable.
- Take a list and initialize it with an empty value using [] or list() to say gvnmatrix.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop
- Inside the For loop, Give all the row elements of the given Matrix as a list using the list(),map(),int(),split() functions and store it in a variable.
- Add the above row elements list to gvnmatrix using the append() function.
- Take a variable say mtrxtrace which stores the trace of the given matrix and initialize its value to 0.
- Take a variable say mtrxsum which stores the sum of all elements of the matrix and initialize its value to 0.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of columns using another Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
- Check if the parent loop iterator value is equal to the inner loop iterator value using the if conditional statement(This is whether the element is diagonal element or not)
- If it is true then add this value to mtrxtrace.
- After the if conditional statement, Add the gvnmatrix[n][m] to the above-initialized mtrxsum and store it in the same variable mtrxsum.
- After the end of two loops calculate the square root of the mtrxsum value using the sqrt() function and store this result in mtrxnormal variable.
- Print the value of mtrxtrace which gives the value of the trace of the given matrix.
- Print the value of mtrxnormal which gives the value of the normal of the given matrix.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import the math module using the import keyword.
import math
# Give the number of rows of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function
# and store it in a variable.
mtrxrows = int(input('Enter some random number of rows of the matrix = '))
# Give the number of columns of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function
# and store it in another variable.
mtrxcols = int(input('Enter some random number of columns of the matrix = '))
# Take a list and initialize it with an empty value using [] or list() to say gvnmatrix.
mtrx = []
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, Give all the row elements of the given Matrix as a list using
# the list(),map(),int(),split() functions and store it in a variable.
l = list(map(int, input(
'Enter {'+str(mtrxcols)+'} elements of row {'+str(n+1)+'} separated by spaces = ').split()))
# Add the above row elements list to gvnmatrix using the append() function.
mtrx.append(l)
# Take a variable say mtrxtrace which stores the trace of the given matrix
# and initialize its value to 0.
mtrxtrace = 0
# Take a variable say mtrxsum which stores the sum of all elements of the matrix
# and initialize its value to 0.
mtrxsum = 0
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of columns using another
# Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
for m in range(mtrxcols):
# Check if the parent loop iterator value is equal to the inner loop iterator value
# using the if conditional statement
# (This is whether the element is diagonal element or not)
if(n == m):
# If it is true then add this value to mtrxtrace.
mtrxtrace = mtrxtrace+mtrx[n][m]
# After the if conditional statement,
# Add the gvnmatrix[n][m] to the above-initialized mtrxsum
# and store it in the same variable mtrxsum.
mtrxsum = mtrxsum+mtrx[n][m]
# After the end of two loops calculate the square root of the mtrxsum value
# using the sqrt() function
# and store this result in mtrxnormal variable.
mtrxnormal = math.sqrt(mtrxsum)
# Print the value of mtrxtrace which gives the value of the trace of the given matrix.
print('The trace value of the given matrix is :', mtrxtrace)
# Print the value of mtrxnormal which gives the value of the normal of the given matrix.
print('The normal value of the given matrix is :', mtrxnormal)
Output:
Enter some random number of rows of the matrix = 4
Enter some random number of columns of the matrix = 4
Enter {4} elements of row {1} separated by spaces = 1 2 3 4
Enter {4} elements of row {2} separated by spaces = 7 5 8 6
Enter {4} elements of row {3} separated by spaces = 9 4 2 5
Enter {4} elements of row {4} separated by spaces = 1 1 1 1
The trace value of the given matrix is : 9
The normal value of the given matrix is : 7.745966692414834Dive into numerous Python Programming Language Examples for practice and get the best out of the tutorial and learn python one step at a time.










