Python Numpy: flatten() vs ravel() | Difference between the ravel numpy and flatten numpy functions
In this tutorial, python beginners and experts can easily learn about the difference between numpy ravel and flatten functions. The main aim of both numpy.ravel() and numpy.flatten() functions are the same i.e. to flatten a numpy array of any shape. Before learning about flatten ravel differences, let’s take a look at the basic overview of both the numpy functions from here.
numpy.ravel()
ravel() is a built-in function in the module of numpy that returns a view of the original array and also returns a flattened 1D view of the numpy array object. Moreover, it accepts an array-like element as a parameter.
Syntax of the ravel() function in numpy:
numpy.ravel(a, order='C')
numpy.ndarray.flatten()
Flatten always returns a copy. The function of the flatten() is a faster member function of the numpy array where it returns a flattened 1D copy of the numpy array object.
Syntax of Numpy flatten() function:
ndarray.flatten(order='C')
Let’s discuss some of the differences between the numpy ravel & flatten function:
Differences between ravel() & flatten()
First of all, import the numpy module,
import numpy as np
A quick view about the difference between flatten and ravel functions in numpy is furnished below:
a.flatten()
(i) Return copy of the original array
(ii) If you modify any value of this array value of the original array is not affected.
(iii) Flatten() is comparatively slower than ravel() as it occupies memory.
(iv) Flatten is a method of a ndarray object.
a.ravel()
(i) Return only reference/view of original array
(ii) If you modify the array you would notice that the value of the original array also changes.
(iii) Ravel is faster than flatten() as it does not occupy any memory.
(iv) Ravel is a library-level function.
For in-depth knowledge on the difference between flatten and ravel numpy functions, kindly check out the further sections without any fail.
Difference 1: Performance: Copy vs view
Thenumpy.ndarray.flatten()function returns a flatten copy of numpy array object only, whereas numpy.ravel() returns a flattened view of the input array if possible.
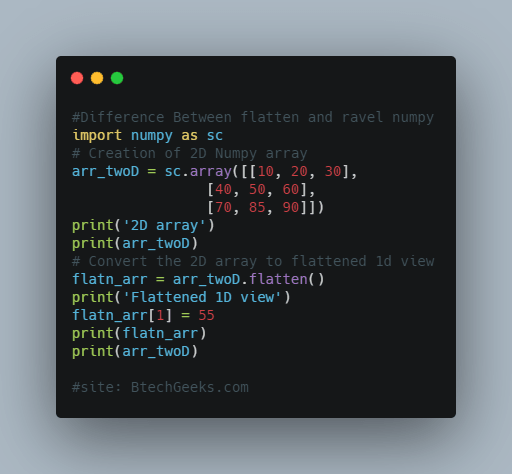
import numpy as sc
# Creation of 2D Numpy array
arr_twoD = sc.array([[10, 20, 30],
[40, 50, 60],
[70, 85, 90]])
print('2D array')
print(arr_twoD)
# Convert the 2D array to flattened 1d view
flatn_arr = arr_twoD.flatten()
print('Flattened 1D view')
flatn_arr[1] = 55
print(flatn_arr)
print(arr_twoD)
Output : 2D array [[10 20 30] [40 50 60] [70 85 90]] Flattened 1D view [10 55 30 40 50 60 70 85 90] [[10 20 30] [40 50 60] [70 85 90]]
Here we can successfully change 2nd element of the numpy array that is reflected in the 1D numpy array. But the original 2D array is unaffected which denotes that flatten() returns a copy of the input array.
Let’s try using numpy.ravel() to convert 2D numpy array to 1D array
ravel() returns a flattened view of the numpy array object if possible. When there is any change done in the view object it will also get reflected in the original numpy array.
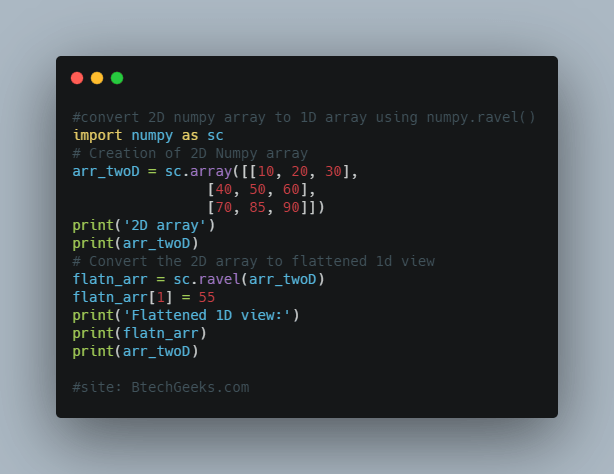
import numpy as sc
# Creation of 2D Numpy array
arr_twoD = sc.array([[10, 20, 30],
[40, 50, 60],
[70, 85, 90]])
print('2D array')
print(arr_twoD)
# Convert the 2D array to flattened 1d view
flatn_arr = sc.ravel(arr_twoD)
flatn_arr[1] = 55
print('Flattened 1D view:')
print(flatn_arr)
print(arr_twoD)
Output : 2D array [[10 20 30] [40 50 60] [70 85 90]] Flattened 1D view: [10 55 30 40 50 60 70 85 90] [[10 55 30] [40 50 60] [70 85 90]]
We can check of the ravel()function returns a view object or not by using the base attribute of the returned object. If it is None then it returns to the original numpy array i.e. it returns a flattened array which is a view only.
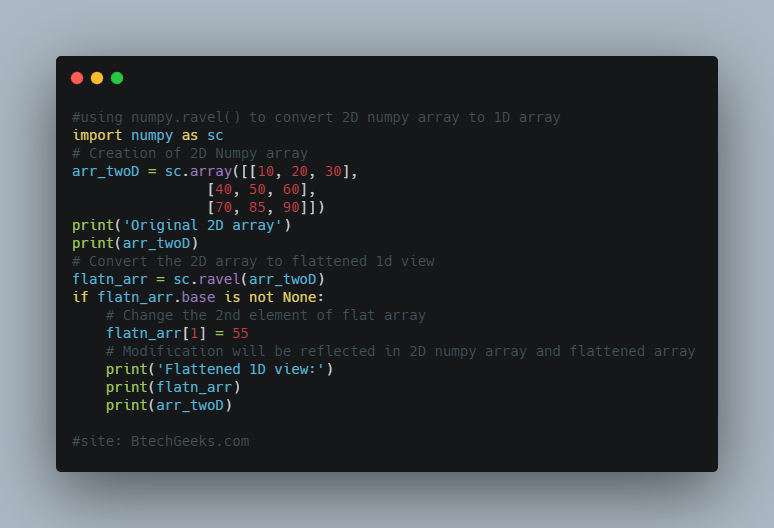
import numpy as sc
# Creation of 2D Numpy array
arr_twoD = sc.array([[10, 20, 30],
[40, 50, 60],
[70, 85, 90]])
print('Original 2D array')
print(arr_twoD)
# Convert the 2D array to flattened 1d view
flatn_arr = sc.ravel(arr_twoD)
if flatn_arr.base is not None:
# Change the 2nd element of flat array
flatn_arr[1] = 55
# Modification will be reflected in 2D numpy array and flattened array
print('Flattened 1D view:')
print(flatn_arr)
print(arr_twoD)
Output : Original 2D array [[10 20 30] [40 50 60] [70 85 90]] Flattened 1D view: [10 55 30 40 50 60 70 85 90] [[10 55 30] [40 50 60] [70 85 90]]
So ravel() returns a view of the input array and hence here the performance of ravel() is better than flatten().
Difference 2: Compatibility with other array-like sequences (list etc)
The ndarray.flatten()function can be used to flatten a numpy array object only. In the case of a numpy.ravel()function being a built-in function, it accepts an array-like element, so we can even pass a list to it.
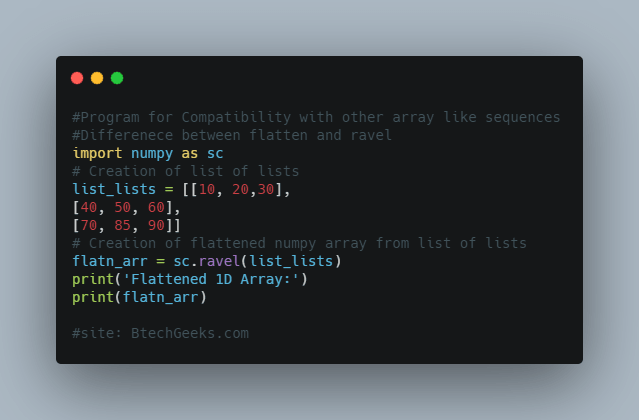
import numpy as sc
# Creation of list of lists
list_lists = [[10, 20,30],
[40, 50, 60],
[70, 85, 90]]
# Creation of flattened numpy array from list of lists
flatn_arr = sc.ravel(list_lists)
print('Flattened 1D Array:')
print(flatn_arr)Output : Flattened 1D Array: [10 20 30 40 50 60 70 85 90]
While this is not feasible with ndarray.flatten() function.
Conclusion on A view of the original array using numpy ravel
Therefore, to conclude in the end there are 2 main differences between the ndarray.flatten() and numpy.ravel() function,
- ravel() function returns a view of the array if possible, where flatten() always returns a copy. Therefore the performance of ravel() is much better than flatten()
- ravel() function can accept other array-like elements like lists etc. Although, flatten() can work with numpy arrays only.