numpy.append() – How to append Elements at the end of numpy array in Python
How to append elements at the end on a Numpy Array in python using numpy.append() in python ?
In this article we will discuss about how to append elements at the end on a Numpy array in python using numpy.append() method.
numpy.append() :
In python, numpy.append() is provided by Numpy module, by using which we can append elements to the end of a Numpy Array.
Syntax : numpy.append(arr, values, axis=None)
where,
- arr : refers to the numpy array where the values will be added.
- values : refers to values that needs to be added.
- axis : refers to axis along which values will be added to array where default value is None. If axis is None then values array will be flattened and values will be added to array. If axis is 0 then value add will occur row wise and if axis is 1 then value add will occur column wise.
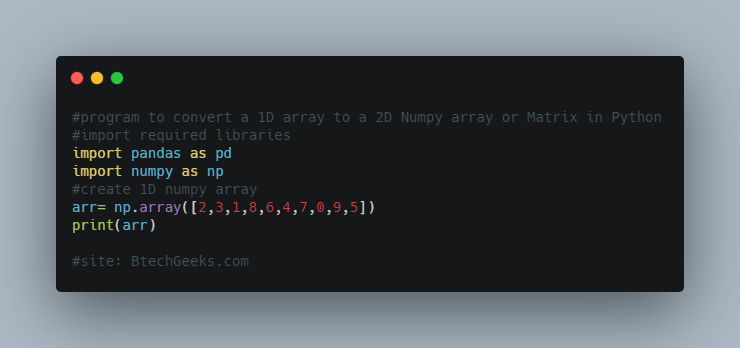
Append elements at the end of 1D numpy array :
#Program import numpy as np # create a Numpy array from a list arr = np.array([11, 22, 33]) #appending a single element to the numpy array new_arr = np.append(arr, 88) print(new_arr)
Output : [11 22 33 88]
Append elements from a list to the Numpy array :
#Program import numpy as np # create a Numpy array from a list arr = np.array([11, 22, 33]) #appending multiple elements to the numpy array new_arr = np.append(arr, [66,77,88]) print(new_arr)
Output : [11 22 33 66 77 88]
Flatten 2D Numpy Array and append items to it :
#Program
import numpy as np
# creating a 2D a Numpy array from a list
arr = np.array( [ [11, 22, 23],
[ 44, 55, 66] ])
#By flattening adding elements in List to 2D Numpy array
new_arr = np.append(arr, [77,88,99])
print(new_arr)Output : [11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99]
Add a Numpy Array to another array row wise :
As we will add Numpy array to another array row wise then we have to set axis as 1=0.
So, let’s see an example how actually it works.
#Program
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D Numpy Array like Matrix
matrix_array1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
matrix_array2 = np.array([[7, 8, 9],
[11, 12, 13]])
#values will be added row wise as axis is 0
new_arr = np.append(matrix_array1, matrix_array2 , axis=0)
print(new_arr)Output : [[1, 2, 3] [4, 5, 6] [7, 8, 9] [11, 12, 13]]
Add a NumPy Array to another array – Column Wise :
As we will add Numpy array to another array row wise then we have to set axis as 1=0.
So, let’s see an example how actually it works.
#Program
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D Numpy Array like Matrix
matrix_array1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
matrix_array2 = np.array([[7, 8, 9],
[11, 12, 13]])
#values ill be added column wise as axis is 0
new_arr = np.append(matrix_array1, matrix_array2 , axis=1)
print(new_arr)Output :
numpy.append() – How to append Elements at the end of numpy array in Python Read More »