Python Program to Find the Position of an Element in a Matrix
In the previous article, we have discussed Python Program to Find the Maximum Element in the Matrix
Given a matrix and a number(element) the task is to find the position of the given element in the given matrix in Python.
If the element does not exist in the given matrix then print the given element doesn’t exist in the given matrix.
If there are multiple answers we print all of them.
What is a matrix:
A matrix is a rectangular sequence of numbers divided into columns and rows. A matrix element or entry is a number that appears in a matrix.
Example:
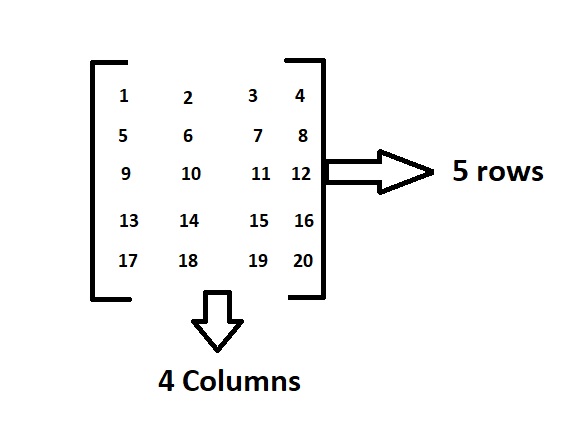
Above is the matrix which contains 5 rows and 4 columns and having elements from 1 to 20.
In this order, the dimensions of a matrix indicate the number of rows and columns.
Here as there are 5 rows and 4 columns it is called a 5*4 matrix.
Examples:
Example1:
Input:
Given Matrix : 2 9 1 11 4 5 9 2 3 1 2 3 Given Element = 9
Output:
The given element { 9 } is present at row {1} and column {2}
The given element { 9 } is present at row {3} and column {1}Example2:
Input:
Given Matrix : 1 2 3 4 Given Element =5
Output:
The given element doesnot exist in the given matrix.
Example3:
Input:
Given Matrix : 2 5 6 1 2 3 Given Element = 5
Output:
The given element { 5 } is present at row {1} and column {2}Program to Find the Position of an Element in a Matrix in Python
Below are the ways to find the position of the given element in the given matrix in Python.
Method #1: Using For Loop (Static Input)
Approach:
- Give the matrix as static input and store it in a variable.
- Calculate the number of rows of the given matrix by calculating the length of the nested list using the len() function and store it in a variable mtrxrows.
- Calculate the number of columns of the given matrix by calculating the length of the first list in the nested list using the len() function and store it in a variable mtrxcolums.
- Give the number/element as static input and store it in a variable to say gvnele.
- Take a variable to say tempo and initialize its value to 0 (Here tempo as temp variable which says whether the element is present or not in matrix at the end).
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of rows using another Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
- Check if the gvnmatrix[n][m] value (where n is the iterator value of the parent For loop and m is the iterator value of the inner For loop) is equal to gvnele using the if conditional statement.
- If it is true then print the iterator value of parent for loop+1(Here it acts as row number) and also print the inner loop iterator value+1(Here it acts as column number).
- Set the value of tempo to 1.
- After the end of loops check if the value of tempo is 0 or not using the if conditional statement.
- If it is true then print the given element doesn’t exist in the given matrix.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Give the matrix as static input and store it in a variable.
mtrx = [[2, 9, 1], [11, 4, 5], [9, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]]
# Calculate the number of rows of the given matrix by
# calculating the length of the nested list using the len() function
# and store it in a variable mtrxrows.
mtrxrows = len(mtrx)
# Calculate the number of columns of the given matrix by
# calculating the length of the first list in the nested list
# using the len() function and store it in a variable mtrxcols.
mtrxcols = len(mtrx[0])
# Give the number/element as static input and store it in a variable to say gvnele.
gvnele = 9
# Take a variable to say tempo and initialize its value to 0
# (Here tempo as temp variable which says whether the element is present
# or not in matrix at the end).
tempo = 0
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of rows using another
# Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
for m in range(mtrxcols):
# Check if the gvnmatrix[n][m] value
# (where n is the iterator value of the parent For loop and
# m is the iterator value of the inner For loop)
# is equal to gvnele using the if conditional statement.
if(mtrx[n][m] == gvnele):
# If it is true then print the iterator value of parent for loop+1
# (Here it acts as row number)
# and also print the inner loop iterator value+1
# (Here it acts as column number).
print('The given element {', gvnele, '} is present at row {' +
str(n+1)+'} and column {'+str(m+1)+'}')
# Set the value of tempo to 1.
tempo = 1
# After the end of loops check if the value of tempo is 0
# or not using the if conditional statement.
if(tempo == 0):
# If it is true then print the given element doesn't exist in the given matrix.
print('the given element doesnot exist in the given matrix.')
Output:
The given element { 9 } is present at row {1} and column {2}
The given element { 9 } is present at row {3} and column {1}Here element 9 is present in two positions so we print two of them.
Method #2: Using For loop (User Input)
Approach:
- Give the number of rows of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function and store it in a variable.
- Give the number of columns of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function and store it in another variable.
- Take a list and initialize it with an empty value using [] or list() to say gvnmatrix.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop
- Inside the For loop, Give all the row elements of the given Matrix as a list using the list(),map(),int(),split() functions and store it in a variable.
- Add the above row elements list to gvnmatrix using the append() function.
- Take a variable to say tempo and initialize its value to 0 (Here tempo as temp variable which says whether the element is present or not in matrix at the end).
- Give the number/element as user input using the int(input()) function and store it in a variable to say gvnele.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of rows using another Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
- Check if the gvnmatrix[n][m] value (where n is the iterator value of the parent For loop and m is the iterator value of the inner For loop) is equal to gvnele using the if conditional statement.
- If it is true then print the iterator value of parent for loop+1(Here it acts as row number) and also print the inner loop iterator value+1(Here it acts as column number).
- Set the value of tempo to 1.
- After the end of loops check if the value of tempo is 0 or not using the if conditional statement.
- If it is true then print the given element doesn’t exist in the given matrix.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Give the number of rows of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function
# and store it in a variable.
mtrxrows = int(input('Enter some random number of rows of the matrix = '))
# Give the number of columns of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function
# and store it in another variable.
mtrxcols = int(input('Enter some random number of columns of the matrix = '))
# Take a list and initialize it with an empty value using [] or list() to say gvnmatrix.
mtrx = []
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, Give all the row elements of the given Matrix as a list using
# the list(),map(),int(),split() functions and store it in a variable.
l = list(map(int, input(
'Enter {'+str(mtrxcols)+'} elements of row {'+str(n+1)+'} separated by spaces = ').split()))
# Add the above row elements list to gvnmatrix using the append() function.
mtrx.append(l)
# Give the number/element as user input using the int(input()) function
# and store it in a variable to say gvnele.
gvnele = int(input('Enter some random element = '))
# Take a variable to say tempo and initialize its value to 0
# (Here tempo as temp variable which says whether the element is present
# or not in matrix at the end).
tempo = 0
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of rows using another
# Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
for m in range(mtrxcols):
# Check if the gvnmatrix[n][m] value
# (where n is the iterator value of the parent For loop and
# m is the iterator value of the inner For loop)
# is equal to gvnele using the if conditional statement.
if(mtrx[n][m] == gvnele):
# If it is true then print the iterator value of parent for loop+1
# (Here it acts as row number)
# and also print the inner loop iterator value+1
# (Here it acts as column number).
print('The given element {', gvnele, '} is present at row {' +
str(n+1)+'} and column {'+str(m+1)+'}')
# Set the value of tempo to 1.
tempo = 1
# After the end of loops check if the value of tempo is 0
# or not using the if conditional statement.
if(tempo == 0):
# If it is true then print the given element doesn't exist in the given matrix.
print('the given element doesnot exist in the given matrix.')
Output:
Enter some random number of rows of the matrix = 2
Enter some random number of columns of the matrix = 3
Enter {3} elements of row {1} separated by spaces = 2 5 6
Enter {3} elements of row {2} separated by spaces = 1 2 3
Enter some random element = 5
The given element { 5 } is present at row {1} and column {2}Output2:(For Reference, if the element doesn’t exist in the matrix)
Enter some random number of rows of the matrix = 2
Enter some random number of columns of the matrix = 2
Enter {2} elements of row {1} separated by spaces = 1 2
Enter {2} elements of row {2} separated by spaces = 3 4
Enter some random element = 5
the given element doesnot exist in the given matrix
Explore more instances related to python concepts from Python Programming Examples Guide and get promoted from beginner to professional programmer level in Python Programming Language.
Python Program to Find the Position of an Element in a Matrix Read More »








