Python Program to Swap Major and Minor Diagonals of a Square Matrix
In the previous article, we have discussed Python Program for Exponential Squaring (Fast Modulo Multiplication)
Given a square matrix, the task is to swap the major diagonal elements and minor diagonal elements of a given matrix.
What is a matrix:
A matrix is a rectangular sequence of numbers divided into columns and rows. A matrix element or entry is a number that appears in a matrix.
Diagonal Matrix:
The entries outside the main diagonal of a diagonal matrix are all 0; the word usually refers to square matrices.
Major Diagonal Matrix :
The Major Diagonal Elements of a Matrix are those that occur from the top left corner of the matrix down to the bottom right corner. The Major Diagonal is also referred to as the Main Diagonal or the Primary Diagonal.
Minor Diagonal Matrix :
Minor Diagonal Elements are those that appear from the top right corner of the matrix down to the bottom left corner. Secondary Diagonal is another name for it.
Example:
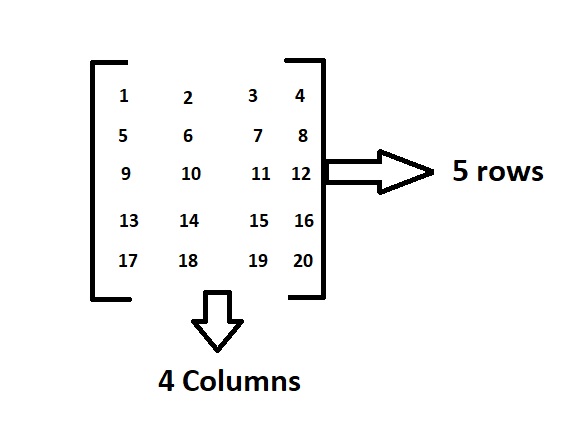
Above is the matrix which contains 5 rows and 4 columns and having elements from 1 to 20.
In this order, the dimensions of a matrix indicate the number of rows and columns.
Here as there are 5 rows and 4 columns it is called a 5*4 matrix.
Examples:
Example1:
Input:
Given Matrix : 6 2 0 1 4 2 3 7 5
Output:
The given matix after swapping the major and the minor diagonal elements: 0 2 6 1 4 2 5 7 3
Example2:
Input:
Given Matrix : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Output:
The given matix after swapping the major and the minor diagonal elements: 3 2 1 4 5 6 9 8 7
Program to Swap Major and Minor Diagonals of a Square Matrix in Python:
Below are the ways to swap the major diagonal elements and minor diagonal elements of a given matrix.
Method #1: Using For Loop (Static Input)
Approach:
- Give the matrix as static input and store it in a variable.
- Calculate the number of rows of the given matrix by calculating the length of the nested list using the len() function and store it in a variable mtrxrows.
- Calculate the number of columns of the given matrix by calculating the length of the first list in the nested list using the len() function and store it in a variable mtrxcolums.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop, swap mtrx[n][n], mtrx[n][mtrxrows-n-1] using the comma(,) operator ( where n is the iterator value and mtrxrows is the no of rows of matrix).
- To print all the elements of the given matrix.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of rows using another Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
- Print the element of the matrix by printing gvnmatrix[n][m] value where n is the iterator value of the parent For loop and m is the iterator value of the inner For loop.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Give the matrix as static input and store it in a variable.
mtrx = [[6, 2, 0], [1, 4, 2], [3, 7, 5]]
# Calculate the number of rows of the given matrix by
# calculating the length of the nested list using the len() function
# and store it in a variable mtrxrows.
mtrxrows = len(mtrx)
# Calculate the number of columns of the given matrix by
# calculating the length of the first list in the nested list
# using the len() function and store it in a variable mtrxcols.
mtrxcols = len(mtrx[0])
print("The given matix after swapping the major and the minor diagonal elements: ")
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, swap mtrx[n][n], mtrx[n][mtrxrows-n-1] using the comma(,) operator
# ( where n is the iterator value and mtrxrows is the no of rows of matrix).
mtrx[n][n], mtrx[n][mtrxrows-n-1] = mtrx[n][mtrxrows-n-1], mtrx[n][n]
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of rows using another
# Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
for m in range(mtrxcols):
# Print the element of the matrix by printing gvnmatrix[n][m] value
# where n is the iterator value of the parent For loop and m is the iterator
# value of the inner For loop.
print(mtrx[n][m], end=' ')
print()
Output:
The given matix after swapping the major and the minor diagonal elements: 0 2 6 1 4 2 5 7 3
Method #2: Using For loop (User Input)
Approach:
- Give the number of rows of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function and store it in a variable.
- Give the number of columns of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function and store it in another variable.
- Take a list and initialize it with an empty value using [] or list() to say gvnmatrix.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop
- Inside the For loop, Give all the row elements of the given Matrix as a list using the list(),map(),int(),split() functions and store it in a variable.
- Add the above row elements list to gvnmatrix using the append() function.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop, swap mtrx[n][n], mtrx[n][mtrxrows-n-1] using the comma(,) operator ( where n is the iterator value and mtrxrows is the no of rows of matrix).
- To print all the elements of the given matrix.
- Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of rows using another Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
- Print the element of the matrix by printing gvnmatrix[n][m] value where n is the iterator value of the parent For loop and m is the iterator value of the inner For loop.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Give the number of rows of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function
# and store it in a variable.
mtrxrows = int(input('Enter some random number of rows of the matrix = '))
# Give the number of columns of the matrix as user input using the int(input()) function
# and store it in another variable.
mtrxcols = int(input('Enter some random number of columns of the matrix = '))
# Take a list and initialize it with an empty value using [] or list() to say gvnmatrix.
mtrx = []
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, Give all the row elements of the given Matrix as a list using
# the list(),map(),int(),split() functions and store it in a variable.
l = list(map(int, input(
'Enter {'+str(mtrxcols)+'} elements of row {'+str(n+1)+'} separated by spaces = ').split()))
# Add the above row elements list to gvnmatrix using the append() function.
mtrx.append(l)
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, swap mtrx[n][n], mtrx[n][mtrxrows-n-1] using the comma(,) operator
# ( where n is the iterator value and mtrxrows is the no of rows of matrix).
mtrx[n][n], mtrx[n][mtrxrows-n-1] = mtrx[n][mtrxrows-n-1], mtrx[n][n]
# Loop till the given number of rows using the For loop.
for n in range(mtrxrows):
# Inside the For loop, Iterate till the given number of rows using another
# Nested For loop(Inner For loop).
for m in range(mtrxcols):
# Print the element of the matrix by printing gvnmatrix[n][m] value
# where n is the iterator value of the parent For loop and m is the iterator
# value of the inner For loop.
print(mtrx[n][m], end=' ')
print()Output:
Enter some random number of rows of the matrix = 3
Enter some random number of columns of the matrix = 3
Enter {3} elements of row {1} separated by spaces = 1 2 3
Enter {3} elements of row {2} separated by spaces = 4 5 6
Enter {3} elements of row {3} separated by spaces = 7 8 9
3 2 1
4 5 6
9 8 7If you are new to the Python Programming Language then practice using our Python Programming Examples for Beginners as our expert team has designed them from scratch.
Python Program to Swap Major and Minor Diagonals of a Square Matrix Read More »