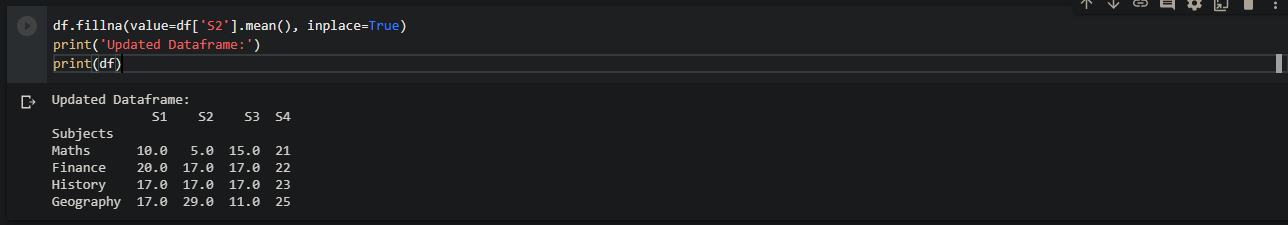
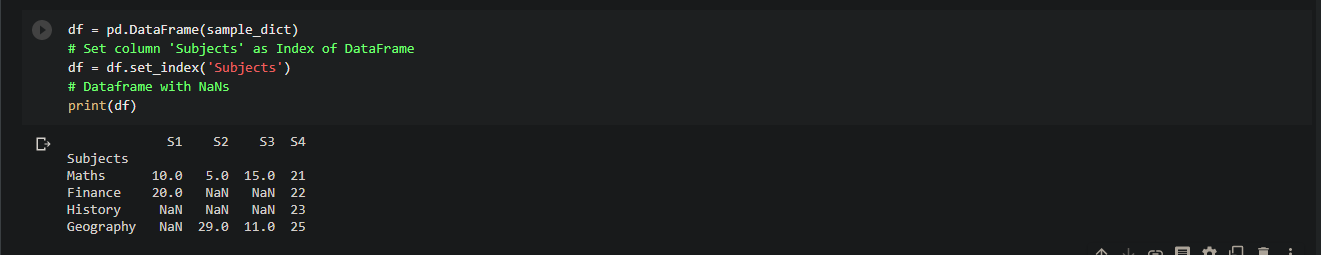
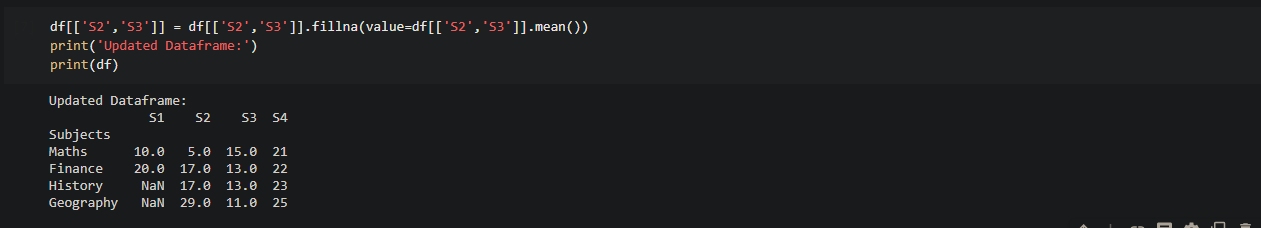
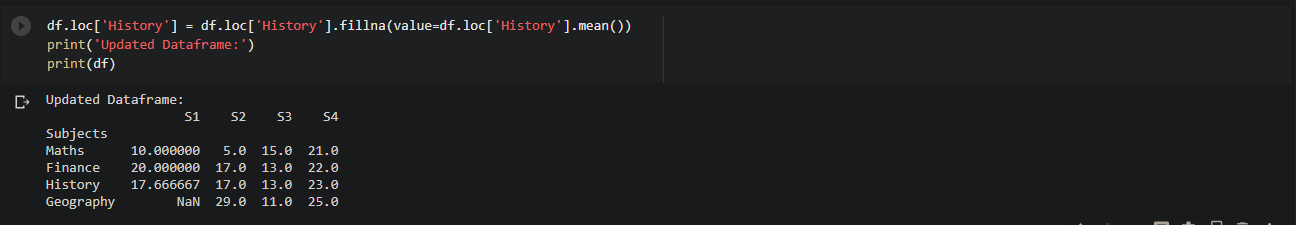
Pandas: Get sum of column values in a Dataframe
How to get the sum of column values in a dataframe in Python ?
In this article, we will discuss about how to get the sum To find the sum of values in a dataframe. So, let’s start exploring the topic.
Select the column by name and get the sum of all values in that column :
To find the sum of values of a single column we have to use the sum( ) or the loc[ ] function.
Using sum() :
Here by using sum( ) only, we selected a column from a dataframe by the column name and from that we can get the sum of values in that column.
Syntax- dataFrame_Object[‘column_name’].sum( )
#Program :
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Example data
students = [('Jill', 16, 'Tokyo', 150),
('Rachel', 38, 'Texas', 177),
('Kirti', 39, 'New York', 97),
('Veena', 40, 'Texas', np.NaN),
('Lucifer', np.NaN, 'Texas', 130),
('Pablo', 30, 'New York', 155),
('Lionel', 45, 'Colombia', 121) ]
dfObj = pd.DataFrame(students, columns=['Name','Age','City','Score'])
#Sum of all values in the 'Score' column of the dataframe
totalSum = dfObj['Score'].sum()
print(totalSum)Output : 830.0
Using loc[ ] :
Here by using loc[] and sum( ) only, we selected a column from a dataframe by the column name and from that we can get the sum of values in that column.
Syntax- dataFrame_Object_name.loc[:, ‘column_name’].sum( )
So, let’s see the implementation of it by taking an example.
#Program :
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Example data
students = [('Jill', 16, 'Tokyo', 150),
('Rachel', 38, 'Texas', 177),
('Kirti', 39, 'New York', 97),
('Veena', 40, 'Texas', np.NaN),
('Lucifer', np.NaN, 'Texas', 130),
('Pablo', 30, 'New York', 155),
('Lionel', 45, 'Colombia', 121) ]
dfObj = pd.DataFrame(students, columns=['Name','Age','City','Score'])
#Sum of all values in the 'Score' column of the dataframe using loc[ ]
totalSum = dfObj.loc[:, 'Score'].sum()
print(totalSum)Output : 830.0
Select the column by position and get the sum of all values in that column :
In case we don’t know about the column name but we know its position, we can find the sum of all value in that column using both iloc[ ] and sum( ). The iloc[ ] returns a series of values which is then passed into the sum( ) function.
So, let’s see the implementation of it by taking an example.
#Program :
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Example data
students = [('Jill', 16, 'Tokyo', 150),
('Rachel', 38, 'Texas', 177),
('Kirti', 39, 'New York', 97),
('Veena', 40, 'Texas', np.NaN),
('Lucifer', np.NaN, 'Texas', 130),
('Pablo', 30, 'New York', 155),
('Lionel', 45, 'Colombia', 121) ]
dfObj = pd.DataFrame(students, columns=['Name','Age','City','Score'])
column_number = 4
# Total sum of values in 4th column i.e. ‘Score’
totalSum = dfObj.iloc[:, column_number-1:column_number].sum()
print(totalSum)Output : Score 830.0 dtype: float64
Find the sum of columns values for selected rows only in Dataframe :
If we need the sum of values from a column’s specific entries we can-
So, let’s see the implementation of it by taking an example.
#Program :
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Example data
students = [('Jill', 16, 'Tokyo', 150),
('Rachel', 38, 'Texas', 177),
('Kirti', 39, 'New York', 97),
('Veena', 40, 'Texas', np.NaN),
('Lucifer', np.NaN, 'Texas', 130),
('Pablo', 30, 'New York', 155),
('Lionel', 45, 'Colombia', 121) ]
dfObj = pd.DataFrame(students, columns=['Name','Age','City','Score'])
column_number = 4
entries = 3
#Sum of the first three values from the 4th column
totalSum = dfObj.iloc[0:entries, column_number-1:column_number].sum()
print(totalSum)Output : Score 424.0 dtype: float64
Find the sum of column values in a dataframe based on condition :
In case we want the sum of all values that follows our conditions, for example scores of a particular city like New York can be found out by –
So, let’s see the implementation of it by taking an example.
#Program :
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Example data
students = [('Jill', 16, 'Tokyo', 150),
('Rachel', 38, 'Texas', 177),
('Kirti', 39, 'New York', 97),
('Veena', 40, 'Texas', np.NaN),
('Lucifer', np.NaN, 'Texas', 130),
('Pablo', 30, 'New York', 155),
('Lionel', 45, 'Colombia', 121) ]
dfObj = pd.DataFrame(students, columns=['Name','Age','City','Score'])
#Sum of all the scores from New York city
totalSum = dfObj.loc[dfObj['City'] == 'New York', 'Score'].sum()
print(totalSum)Output : 252.0