Python Program to Read a File and Capitalize the First Letter of Every Word in the File
Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important Java fundamentals with the Simple java program example guide and practice well.
Files in Python:
A file is a piece of information or data that is kept in computer storage devices. You are already familiar with several types of files, such as music files, video files, and text files. Python makes it simple to manipulate these files. In general, files are classified into two types: text files and binary files. Text files are plain text, whereas binary files include binary data that can only be read by a computer.
Python file handling (also known as File I/O) is an important topic for programmers and automation testers. It is necessary to work with files in order to either write to or read data from them.
Furthermore, if you are not already aware, I/O operations are the most expensive procedures through which a program might fail. As a result, you should take caution while implementing file handling for reporting or any other reason. Optimizing a single file activity can contribute to the development of a high-performance application or a solid solution for automated software testing.
Given a file, thee= task is to read the given file and capitalize the first letter of every word in the given file
Program to Read a File and Capitalize the First Letter of Every Word in the File
Below is the full process Read a File and Capitalize the First Letter of Every Word in the File.
Approach:
- Create the file or upload the existing file.
- Enter the file name of the file using the input() function and store it in a variable.
- In read mode, open the file with the entered file name.
- Using for loop, go over the lines in the first file.
- To capitalize each word in the line, use the title() function.
- Print the file’s modified lines.
- The exit of the program.
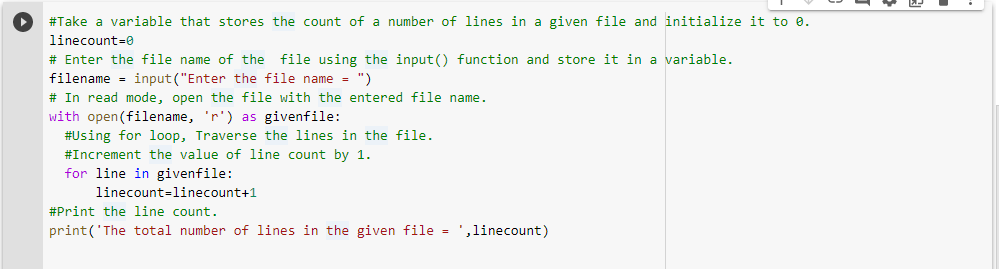
Below is the implementation:
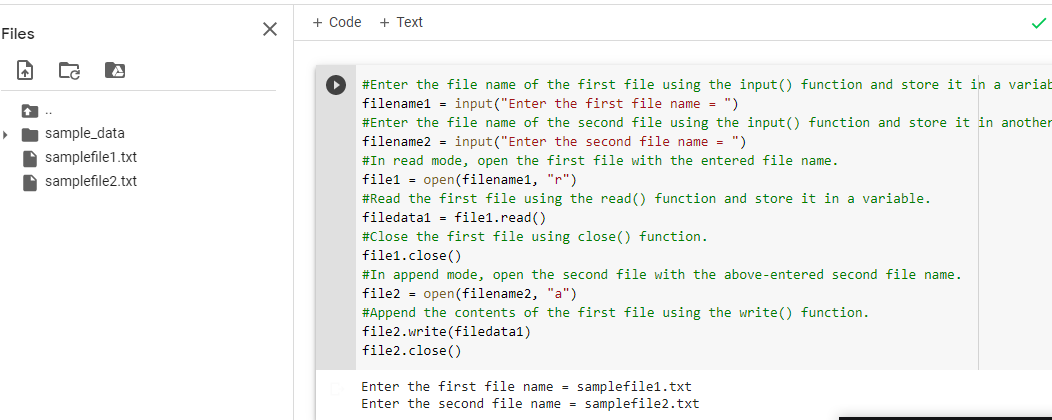
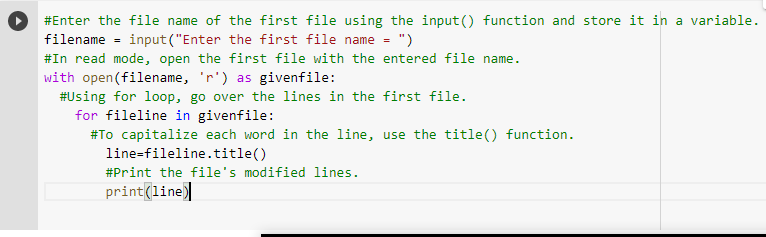
# Enter the file name of the first file using the input() function and store it in a variable.
filename = input("Enter the first file name = ")
# In read mode, open the first file with the entered file name.
with open(filename, 'r') as givenfile:
# Using for loop, go over the lines in the first file.
for fileline in givenfile:
# To capitalize each word in the line, use the title() function.
line = fileline.title()
# Print the file's modified lines.
print(line)
Explanation:
- A file name needs to be entered by the user.
- The file is opened in reading mode with the open() function.
- To read every line in the file, a for loop is needed.
- The title() method is used to capitalize every word in the line.
- The modified lines will be printed.
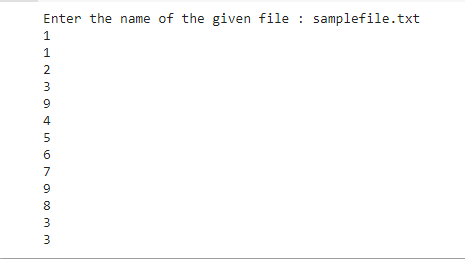
Output:
Before Modifying:
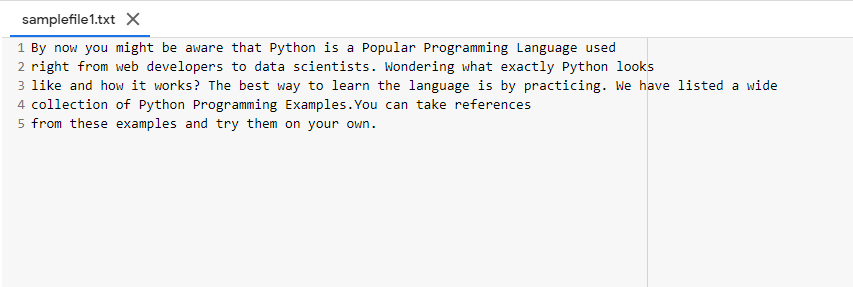
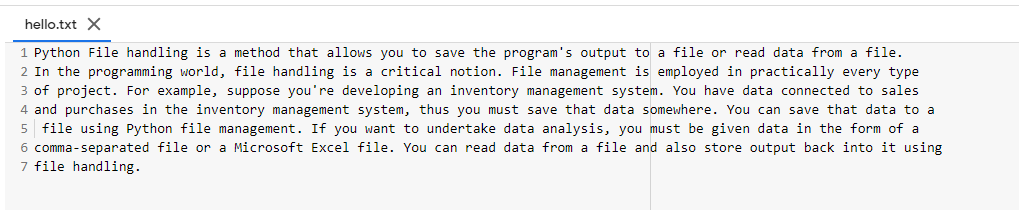
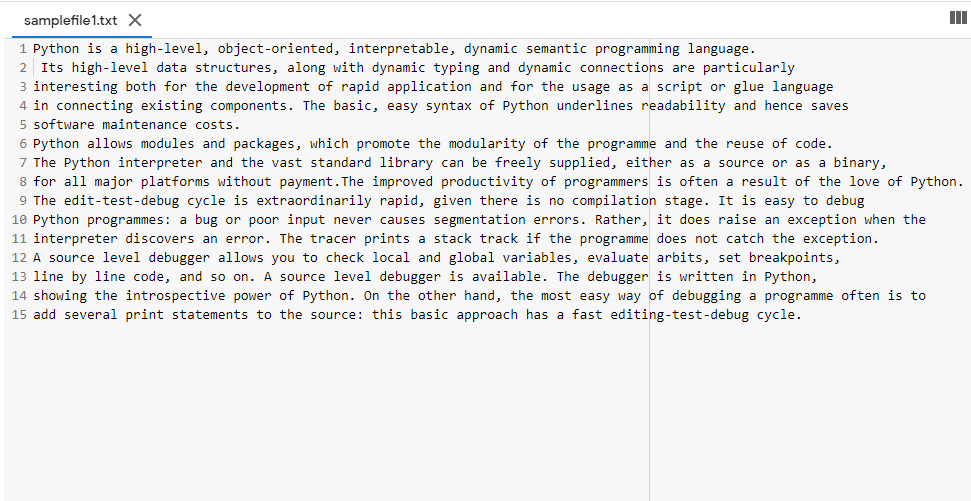
Python is a high-level, object-oriented, interpretable, dynamic semantic programming language. Its high-level data structures, along with dynamic typing and dynamic connections are particularly interesting both for the development of rapid application and for the usage as a script or glue language in connecting existing components. The basic, easy syntax of Python underlines readability and hence saves software maintenance costs. Python allows modules and packages, which promote the modularity of the programme and the reuse of code. The Python interpreter and the vast standard library can be freely supplied, either as a source or as a binary, for all major platforms without payment.The improved productivity of programmers is often a result of the love of Python. The edit-test-debug cycle is extraordinarily rapid, given there is no compilation stage. It is easy to debug Python programmes: a bug or poor input never causes segmentation errors. Rather, it does raise an exception when the interpreter discovers an error. The tracer prints a stack track if the programme does not catch the exception. A source level debugger allows you to check local and global variables, evaluate arbits, set breakpoints, line by line code, and so on. A source level debugger is available. The debugger is written in Python, showing the introspective power of Python. On the other hand, the most easy way of debugging a programme often is to add several print statements to the source: this basic approach has a fast editing-test-debug cycle.
After Modifying:
Enter the first file name = samplefile1.txt Python Is A High-Level, Object-Oriented, Interpretable, Dynamic Semantic Programming Language. Its High-Level Data Structures, Along With Dynamic Typing And Dynamic Connections Are Particularly Interesting Both For The Development Of Rapid Application And For The Usage As A Script Or Glue Language In Connecting Existing Components. The Basic, Easy Syntax Of Python Underlines Readability And Hence Saves Software Maintenance Costs. Python Allows Modules And Packages, Which Promote The Modularity Of The Programme And The Reuse Of Code. The Python Interpreter And The Vast Standard Library Can Be Freely Supplied, Either As A Source Or As A Binary, For All Major Platforms Without Payment.The Improved Productivity Of Programmers Is Often A Result Of The Love Of Python. The Edit-Test-Debug Cycle Is Extraordinarily Rapid, Given There Is No Compilation Stage. It Is Easy To Debug Python Programmes: A Bug Or Poor Input Never Causes Segmentation Errors. Rather, It Does Raise An Exception When The Interpreter Discovers An Error. The Tracer Prints A Stack Track If The Programme Does Not Catch The Exception. A Source Level Debugger Allows You To Check Local And Global Variables, Evaluate Arbits, Set Breakpoints, Line By Line Code, And So On. A Source Level Debugger Is Available. The Debugger Is Written In Python, Showing The Introspective Power Of Python. On The Other Hand, The Most Easy Way Of Debugging A Programme Often Is To Add Several Print Statements To The Source: This Basic Approach Has A Fast Editing-Test-Debug Cycle.
Google Colab Images:
Files and Code:
Code:
 ‘
‘
Output Image:

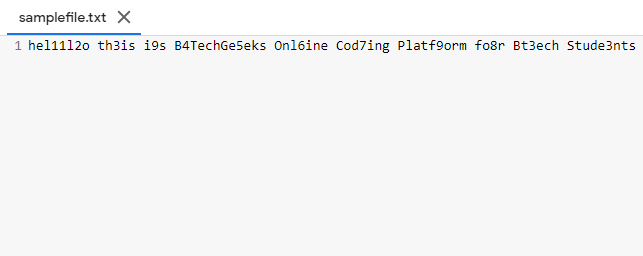
Sample file:
Related Programs:
- Python Program to Append the Contents of One File to Another File
- Python Program to Read a Text File and Print all the Numbers Present in the Text File
- Python Program to Copy the Contents of One File into Another
- Python Program to Count the Number of Words in a Text File
- Python Program to Count the Number of Lines in a Text File
- Python Program to Count the Number of Blank Spaces in a Text File
- Python Program to Count the Occurrences of a Word in a Text File
Python Program to Read a File and Capitalize the First Letter of Every Word in the File Read More »