Pandas: skip rows while reading csv file to a Dataframe using read_csv() in Python
In this tutorial, we will discuss how to skip rows while reading a csv file to a Dataframe using aread_csv()method of Pandas library in Python. If you want you can learn more about the read_csv() method along with syntax, parameters, and various methods to skip rows while reading specific rows from csv in python pandas
- How to skip rows while reading CSV file using Pandas?
- Method 1: Skipping N rows from the starting while reading a csv file
- Method 2: Skipping rows at specific index positions while reading a csv file to Dataframe
- Skipping N rows from top except header while reading a csv file to Dataframe
- Skip rows from based on condition while reading a csv file to Dataframe
- Skip N rows from bottom/footer while reading a csv file to Dataframe
How to skip rows while reading CSV file using Pandas?
Python is a very useful language in today’s time, its also very useful for data analysis because of the different python packages. Python panda’s library implements a function to read a csv file and load data to dataframe quickly and also skip specified lines from csv file. Here we will use theread_csv()method of Pandas to skip n rows. i.e.,
pandas.read_csv(filepath_or_buffer, skiprows=N, ....)
Parameters:
| Parameter | Use |
|---|---|
| filepath_or_buffer | URL or Dir location of file |
| sep | Stands for separator, default is ‘, ‘ as in csv(comma separated values) |
| index_col | This parameter is used to make the passed column as index instead of 0, 1, 2, 3…r |
| header | This parameter is use to make passed row/s[int/int list] as header |
| use_cols | This parameter is only used the passed col[string list] to make a data frame |
| squeeze | If True and only one column is passed then returns pandas series |
| skiprows | This parameter is used to skip passed rows in a new data frame |
| skipfooter | This parameter is used to skip the Number of lines at bottom of the file |
Let’s, import the pandas’ module in python first:
Import pandas as pd
Let’s see the examples mentioned below and learn the process of Pandas: skip rows while reading csv file to a Dataframe using read_csv() in Python. Now, create one simple CSV file instru.csv
Name,Age,City Tara,34,Agra Rekha,31,Delhi Aavi,16,Varanasi Sarita,32,Lucknow Mira,33,Punjab Suri,35,Patna
Also Check:
- Pandas: Convert a dataframe column into a list using Series.to_list() or numpy.ndarray.tolist() in python
- Python Pandas: Select Rows in DataFrame by conditions on multiple columns
Let’s load this csv file to a dataframe using read_csv() and skip rows in various ways,
Method 1: Skipping N rows from the starting while reading a csv file
When we pass skiprows=2 it means it will skip those rows while reading csv file. For example, if we want to skip 2 lines from the top while readingusers.csvfile and initializing a dataframe.
import pandas as pd
# Skip 2 rows from top in csv and initialize a dataframe
usersDf = pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\HP\Desktop\instru.csv", skiprows=2)
print('Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping top 2 lines from csv file ')
print(usersDf)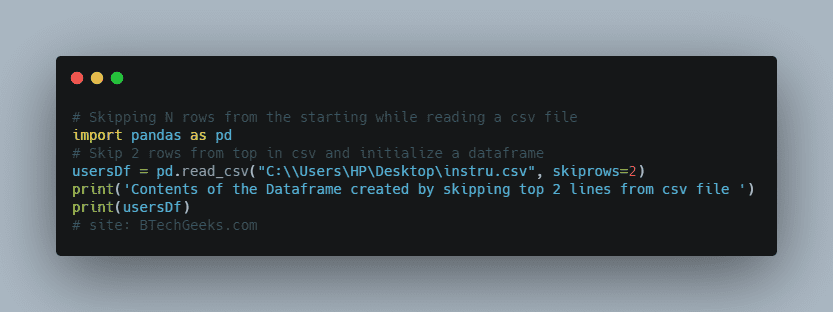
Output:
Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping top 2 lines from csv file Rekha 31 Delhi 0 Aavi 16 Varanasi 1 Sarita 32 Lucknow 2 Mira 33 Punjab 3 Suri 35 Patna
Method 2: Skipping rows at specific index positions while reading a csv file to Dataframe
For skipping rows at specific index positions we have to give index positions like if we want to skip lines at index 0, 2, and 5 in dataframe ‘skiprows=[0,2,5]’.
import pandas as pd
# Skip rows at specific index
usersDf = pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\HP\Desktop\instru.csv", skiprows=[0,2,5])
print('Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping specifying lines from csv file ')
print(usersDf)
Output:
Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping specifying lines from csv file Tara 34 Agra 0 Aavi 16 Varanasi 1 Sarita 32 Lucknow 2 Suri 35 Patna
It skipped all the lines at index positions 0, 2 & 5 from csv and loaded the remaining rows from csv.
Skipping N rows from top except header while reading a csv file to Dataframe
In the earlier example, we have seen that it removes the header also. In this, we want to remove 2 rows from starting but not the header one.
import pandas as pd
# Skip 2 rows from top except header
usersDf = pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\HP\Desktop\instru.csv", skiprows=[i for i in range(1,3)])
print('Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping 2 rows after header row from csv file ')
print(usersDf)
Output:
Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping 2 rows after header row from csv file
Name Age City
0 Aavi 16 Varanasi
1 Sarita 32 Lucknow
2 Mira 33 Punjab
3 Suri 35 Patna
Skip rows from based on condition while reading a csv file to Dataframe
Here we will give some specific conditions using the lambda function for skipping rows in the dataframe.
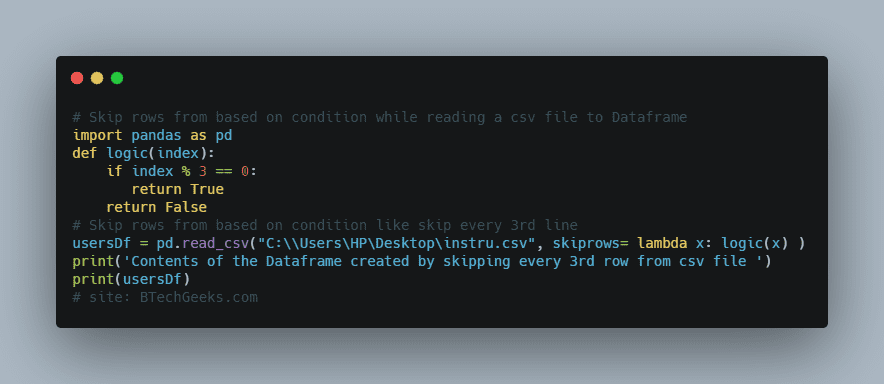
import pandas as pd
def logic(index):
if index % 3 == 0:
return True
return False
# Skip rows from based on condition like skip every 3rd line
usersDf = pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\HP\Desktop\instru.csv", skiprows= lambda x: logic(x) )
print('Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping every 3rd row from csv file ')
print(usersDf)
Output:
Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping every 3rd row from csv file
Tara 34 Agra
0 Rekha 31 Delhi
1 Sarita 32 Lucknow
2 Mira 33 Punjab
Skip N rows from bottom/footer while reading a csv file to Dataframe
So here we use skipfooter & engine argument in pd.read_csv() to skip n rows from the bottom.
import pandas as pd
# Skip 2 rows from bottom
usersDf = pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\HP\Desktop\instru.csv", skipfooter=2, engine='python')
print('Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping bottom 2 rows from csv file ')
print(usersDf)Output:
Contents of the Dataframe created by skipping bottom 2 rows from csv file Name Age City 0 Tara 34 Agra 1 Rekha 31 Delhi 2 Aavi 16 Varanasi 3 Sarita 32 Lucknow
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned different ways of how to skip rows while reading csv file to a Dataframe using the Python pandas read_csv() function.
Want to expert in the python programming language? Exploring Python Data Analysis using Pandas tutorial changes your knowledge from basic to advance level in python concepts.
Similar Tutorials:
Pandas: skip rows while reading csv file to a Dataframe using read_csv() in Python Read More »