Python Program to Find Common Divisors of Two Numbers
Given two numbers the task is to find the common divisors of the given two numbers in Python.
Using a Python program, we will find the common divisors of two numbers. Integers that divide both numbers correctly are known as common divisors. Here, we will learn what common divisors are, how to find them, and how to use Python to find the common divisors of two numbers.
Examples:
Example1:
Input:
Given First Number =56 Given Second Number =88
Output:
The common divisors of the two numbers { 56 88 } are :
1
2
4
8Example2:
Input:
Given First Number =105 Given Second Number =85
Output:
Enter some random first number =105
Enter some random second number =85
The common divisors of the two numbers { 105 85 } are :
1
5Program to Find Common Divisors of Two Numbers in Python
Below are the ways to find the common divisors of the given two numbers in Python.
Have you mastered basic programming topics of java and looking forward to mastering advanced topics in a java programming language? Go with these ultimate Advanced java programs examples with output & achieve your goal in improving java coding skills.
Method #1: Using For Loop (Static Input)
Approach:
- Give the first number as static input and store it in a variable.
- Give the second number as static input and store it in another variable.
- Calculate the minimum number among the two numbers using the min() function and store it in a variable.
- Loop from 1 to minimum number using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop.
- Check if the iterator value divides the given two numbers using the If conditional Statement.
- If it is true then print the iterator value.
- The Exit of the Program.
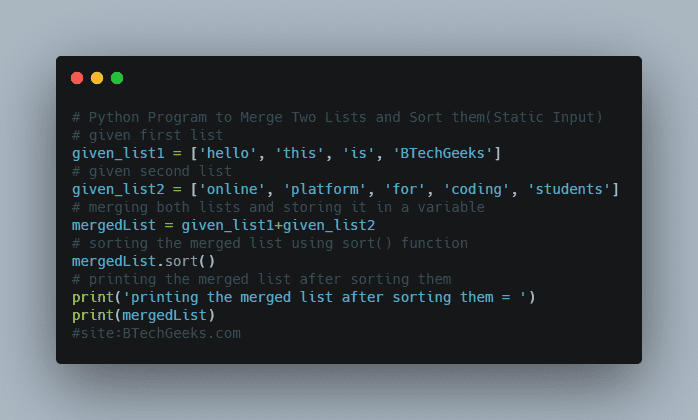
Below is the implementation:
# Give the first number as static input and store it in a variable.
firstnumbe = 56
# Give the second number as static input and store it in another variable.
secondnumbe = 88
# Calculate the minimum number among the two numbers using the min()
# function and store it in a variable.
mininumb = min(firstnumbe, secondnumbe)
print(
'The common divisors of the two numbers {', firstnumbe, secondnumbe, '} are :')
# Loop from 1 to minimum number using the For loop.
for itrnumb in range(1, mininumb+1):
# Inside the For loop.
# Check if the iterator value divides the given two numbers
# using the If conditional Statement.
if(firstnumbe % itrnumb == 0 and secondnumbe % itrnumb == 0):
# If it is true then print the iterator value.
print(itrnumb)
Output:
The common divisors of the two numbers { 56 88 } are :
1
2
4
8Method #2: Using For Loop (User Input)
Approach:
- Give the first number as the user input using the int(input()) function and store it in a variable.
- Give the second number as the user input using the int(input()) function and store it in another variable.
- Calculate the minimum number among the two numbers using the min() function and store it in a variable.
- Loop from 1 to minimum number using the For loop.
- Inside the For loop.
- Check if the iterator value divides the given two numbers using the If conditional Statement.
- If it is true then print the iterator value.
- The Exit of the Program.
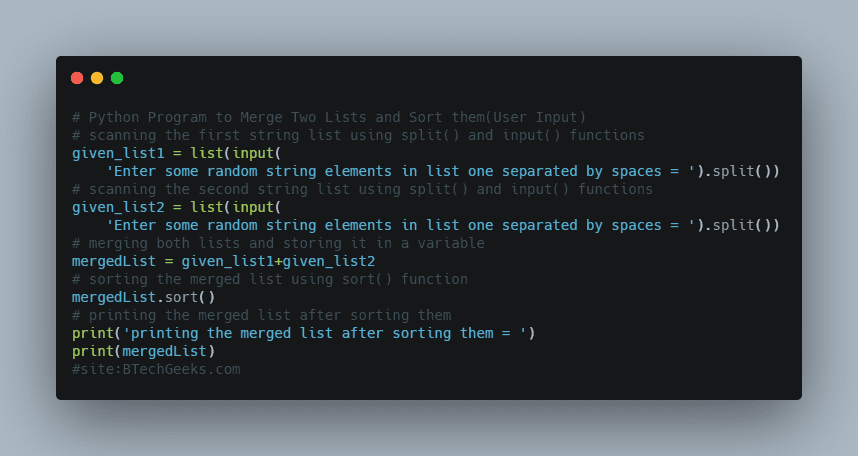
Below is the implementation:
# Give the first number as the user input using the int(input())
# function and store it in a variable.
firstnumbe = int(input('Enter some random first number ='))
# Give the second number as the user input using the int(input())
# function and store it in another variable.
secondnumbe = int(input('Enter some random second number ='))
# Calculate the minimum number among the two numbers using the min()
# function and store it in a variable.
mininumb = min(firstnumbe, secondnumbe)
print(
'The common divisors of the two numbers {', firstnumbe, secondnumbe, '} are :')
# Loop from 1 to minimum number using the For loop.
for itrnumb in range(1, mininumb+1):
# Inside the For loop.
# Check if the iterator value divides the given two numbers
# using the If conditional Statement.
if(firstnumbe % itrnumb == 0 and secondnumbe % itrnumb == 0):
# If it is true then print the iterator value.
print(itrnumb)
Output:
Enter some random first number =105
Enter some random second number =85
The common divisors of the two numbers { 105 85 } are :
1
5Related Programs:
- python program to find the product of two numbers using recursion
- python program to find the lcm of two numbers using recursion
- python program to find the sum of natural numbers
- python program to find whether a number is a power of two
- python program to find those numbers which are divisible by 7 and multiple of 5 in a given range of numbers
- python program to find all numbers in a range which are perfect squares and sum of all digits in the number is less than 10
- python program to find the minimum difference between the index of two given elements present in an array
Python Program to Find Common Divisors of Two Numbers Read More »