Python Program to Compute the Area and Perimeter of Octagon
In the previous article, we have discussed Python Program to Compute the Area and Perimeter of Heptagon
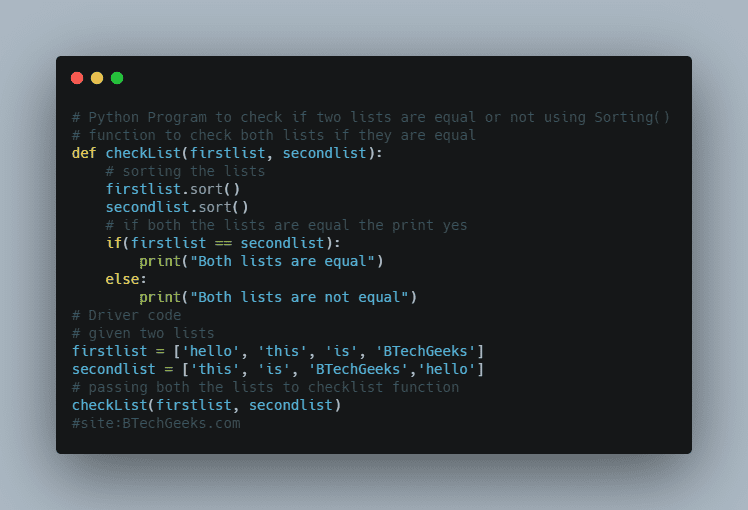
Math Module :
Python’s math module is a built-in module. By importing this module, we can perform mathematical computations.
Numerous mathematical operations like ceil( ),floor( ),factorial( ),mod( ),value of pi ,…..etc .can be computed with the help of math module.
Octagon:
An octagon is a polygon with eight sides. It has eight different angles.
Octagon = octa + gon, where octa is the number eight and gon is the number of sides.
In an octagon, there are 20 diagonals.
Formula to calculate the area of an Octagon:
Example1:
Input:
Given The Octagon's side length = 6
Output:
The Octagon's Area with given side length { 6 } = 173.82337649086284
The Octagon's Perimeter with the given side length { 6 } = 48Example2:
Input:
Given The Octagon's side length = 12.5
Output:
The Octagon's Area with given side length { 12.5 } = 754.4417382415921
The Octagon's Perimeter with the given side length { 12.5 } = 100.0Program to Compute the Area and Perimeter of Octagon
Below are the ways to Calculate the area and perimeter of a heptagon with the given Octagon’s side length:
Method #1: Using Mathematical Formula (Static Input)
Approach:
- Import the math module using the import keyword.
- Give the Octagon’s side length as static input and store it in a variable.
- Calculate the area of the given Octagon using the above given mathematical formula and sqrt(), math.pow() functions.
- Store it in another variable.
- Calculate the perimeter of the given Octagon using the above given mathematical formula.
- Store it in another variable.
- Print the Octagon’s area with the given side length.
- Print the Octagon’s perimeter with the given side length.
- The Exit of the program.
Below is the implementation:
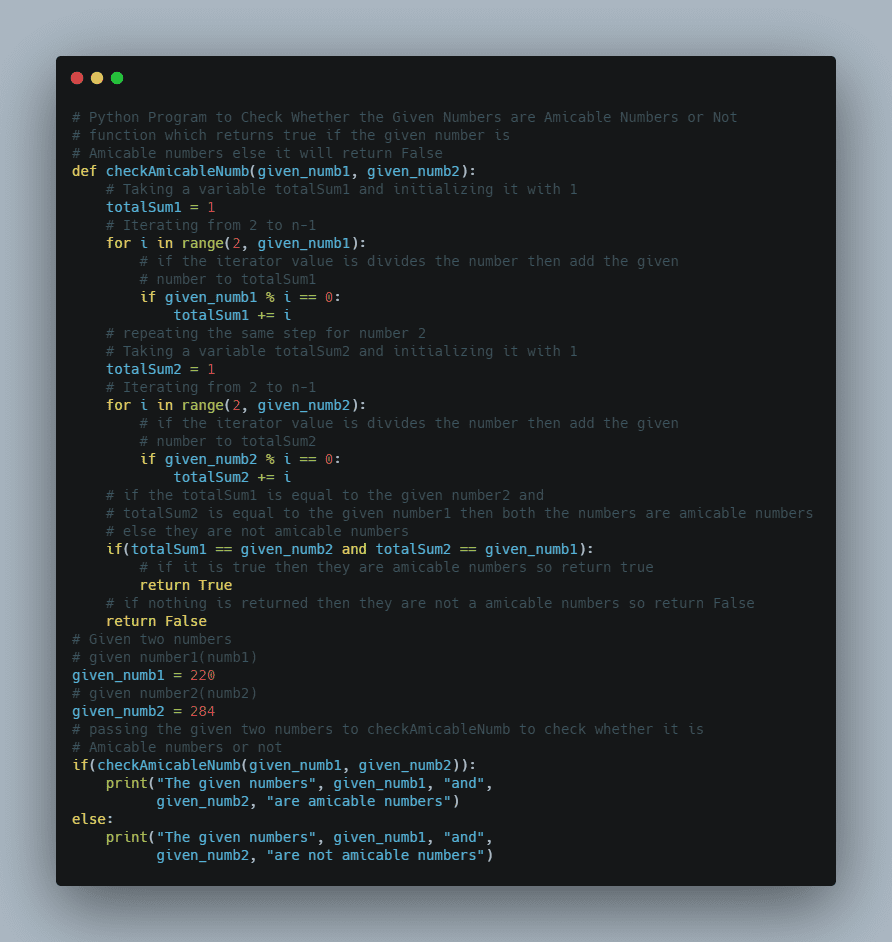
# Import the math module using the import keyword.
import math
# Give the Octagon's side length as static input and store it in a variable.
side_len = 6
# Calculate the area of the given Octagon using the above given mathematical formula
# and sqrt(), math.pow() functions.
# Store it in another variable.
octgn_area = (2*(1+math.sqrt(2))*math.pow(side_len, 2))
# Calculate the perimeter of the given Octagon using the above given mathematical formula.
# Store it in another variable.
octgn_perimetr = (8*side_len)
# Print the Octagon's area with the given side length.
print(
"The Octagon's Area with given side length {", side_len, "} =", octgn_area)
# Print the Octagon's perimeter with the given side length.
print(
"The Octagon's Perimeter with the given side length {", side_len, "} =", octgn_perimetr)
Output:
The Octagon's Area with given side length { 6 } = 173.82337649086284
The Octagon's Perimeter with the given side length { 6 } = 48Method #2: Using Mathematical Formula (User Input)
Approach:
- Import the math module using the import keyword.
- Give the Octagon’s side length as user input using float(input()) function and store it in a variable.
- Calculate the area of the given Octagon using the above given mathematical formula and sqrt(), math.pow() functions.
- Store it in another variable.
- Calculate the perimeter of the given Octagon using the above given mathematical formula.
- Store it in another variable.
- Print the Octagon’s area with the given side length.
- Print the Octagon’s perimeter with the given side length.
- The Exit of the program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import the math module using the import keyword.
import math
# Give the Octagon's side length as user input using float(input()) function and
# store it in a variable.
side_len = float(input("Enter some random number = "))
# Calculate the area of the given Octagon using the above given mathematical formula
# and sqrt(), math.pow() functions.
# Store it in another variable.
octgn_area = (2*(1+math.sqrt(2))*math.pow(side_len, 2))
# Calculate the perimeter of the given Octagon using the above given mathematical formula.
# Store it in another variable.
octgn_perimetr = (8*side_len)
# Print the Octagon's area with the given side length.
print(
"The Octagon's Area with given side length {", side_len, "} =", octgn_area)
# Print the Octagon's perimeter with the given side length.
print(
"The Octagon's Perimeter with the given side length {", side_len, "} =", octgn_perimetr)
Output:
Enter some random number = 12.5
The Octagon's Area with given side length { 12.5 } = 754.4417382415921
The Octagon's Perimeter with the given side length { 12.5 } = 100.0Explore more instances related to python concepts from Python Programming Examples Guide and get promoted from beginner to professional programmer level in Python Programming Language.
Python Program to Compute the Area and Perimeter of Octagon Read More »


![Using [] symbol](https://python-programs.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Using-symbol.png)