Python Program to Compute the Area and Perimeter of Pentagon
In the previous article, we have discussed Python Program to Compute the Area and Perimeter of Octagon
Pentagon:
A pentagon (from the Greek v Pente and gonia, which mean five and angle) is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. A simple pentagon’s internal angles add up to 540°.
A pentagon can be simple or complex, and it can be self-intersecting. A pentagram is a self-intersecting regular pentagon (or a star pentagon).
Formula to calculate the perimeter of a pentagon:
Example1:
Input:
Given The Pentagon's side length = 10
Output:
The Pentagon's area with given side length { 10 } = 172.0477400588967
The Pentagon's Perimeter with given side length { 10 } = 50Example2:
Input:
Given The Pentagon's side length = 5.5
Output:
The Pentagon's area with given side length { 5.5 } = 52.04444136781625
The Pentagon's Perimeter with given side length { 5.5 } = 27.5Program to Compute the Area and Perimeter of Pentagon in Python
Below are the ways to Calculate the area and perimeter of a pentagon with the given Pentagon’s side length:
Method #1: Using Mathematical Formula (Static Input)
Approach:
- Import the math module using the import keyword.
- Give the Pentagon’s side length as static input and store it in a variable.
- Calculate the area of the given pentagon using the above given mathematical formula and math.sqrt() function.
- Store it in another variable.
- Calculate the perimeter of the given pentagon using the above given mathematical formula.
- Store it in another variable.
- Print the Pentagon’s area with the given side length.
- Print the Pentagon’s perimeter with the given side length.
- The Exit of the program.
Below is the implementation:
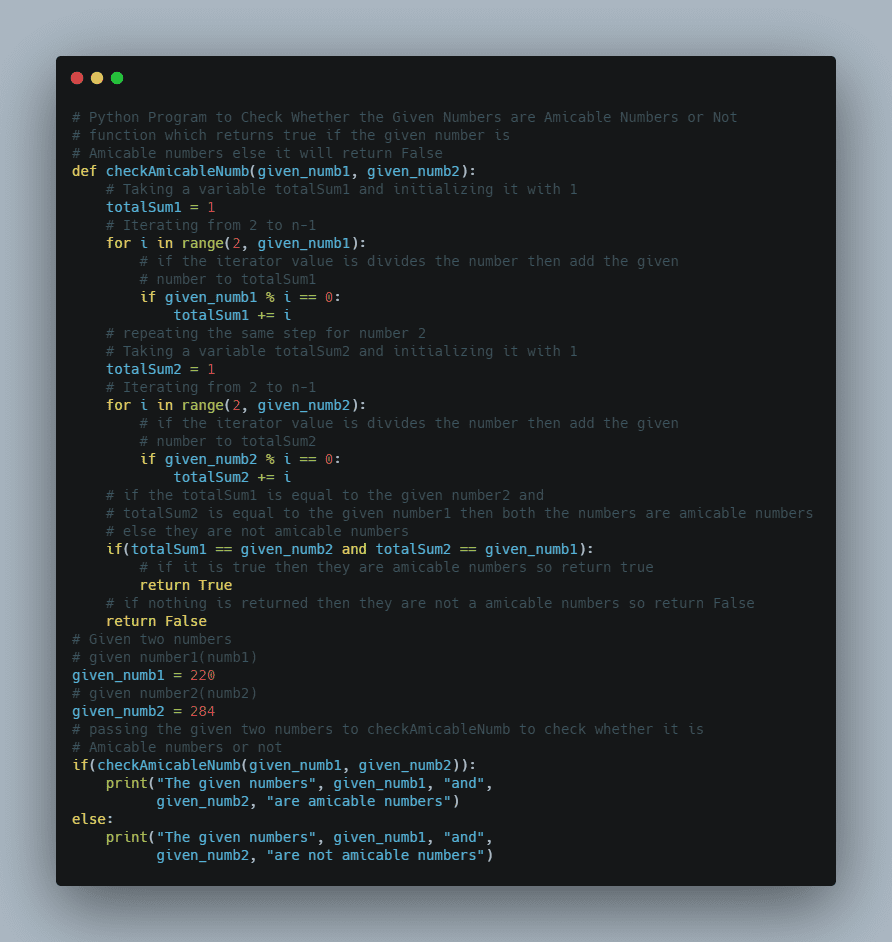
# Import the math module using the import keyword.
import math
# Give the Pentagon's side length as static input and store it in a variable.
side_len = 10
# Calculate the area of the given pentagon using the above given mathematical formula and
# math.sqrt() function.
# Store it in another variable.
pentgn_area = (math.sqrt(5*(5+2*math.sqrt(5)))*pow(side_len, 2))/4.0
# Calculate the perimeter of the given pentagon using the above given mathematical formula.
# Store it in another variable.
pentgn_perimtr = (5*side_len)
# Print the Pentagon's area with the given side length.
print(
"The Pentagon's area with given side length {", side_len, "} =", pentgn_area)
# Print the Pentagon's perimeter with the given side length.
print(
"The Pentagon's Perimeter with given side length {", side_len, "} =", pentgn_perimtr)
Output:
The Pentagon's area with given side length { 10 } = 172.0477400588967
The Pentagon's Perimeter with given side length { 10 } = 50Method #2: Using Mathematical Formula (User Input)
Approach:
- Import the math module using the import keyword.
- Give the Pentagon’s side length as user input using float(input()) function and store it in a variable.
- Calculate the area of the given pentagon using the above given mathematical formula and math.sqrt() function.
- Store it in another variable.
- Calculate the perimeter of the given pentagon using the above given mathematical formula.
- Store it in another variable.
- Print the Pentagon’s area with the given side length.
- Print the Pentagon’s perimeter with the given side length.
- The Exit of the program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import the math module using the import keyword.
import math
# Give the Pentagon's side length as user input using float(input()) function and
# store it in a variable.
side_len = float(input('Enter some random number = '))
# Calculate the area of the given pentagon using the above given mathematical formula and
# math.sqrt() function.
# Store it in another variable.
pentgn_area = (math.sqrt(5*(5+2*math.sqrt(5)))*pow(side_len, 2))/4.0
# Calculate the perimeter of the given pentagon using the above given mathematical formula.
# Store it in another variable.
pentgn_perimtr = (5*side_len)
# Print the Pentagon's area with the given side length.
print(
"The Pentagon's area with given side length {", side_len, "} =", pentgn_area)
# Print the Pentagon's perimeter with the given side length.
print(
"The Pentagon's Perimeter with given side length {", side_len, "} =", pentgn_perimtr)
Output:
Enter some random number = 5.5
The Pentagon's area with given side length { 5.5 } = 52.04444136781625
The Pentagon's Perimeter with given side length { 5.5 } = 27.5Explore more instances related to python concepts from Python Programming Examples Guide and get promoted from beginner to professional programmer level in Python Programming Language.
Python Program to Compute the Area and Perimeter of Pentagon Read More »










![Using [] symbol](https://python-programs.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Using-symbol.png)